如何运行评估
在本指南中,我们将介绍如何使用 LangSmith SDK 中的 evaluate() 方法评估应用程序。
对于 Python 中较大的评估作业,我们建议使用 aevaluate(),即 evaluate() 的异步版本。 在阅读有关异步运行评估的操作指南之前,仍然值得先阅读本指南,因为两者具有相同的接口。
在 JS/TS 中,evaluate() 已经是异步的,因此不需要单独的方法。
配置max_concurrency/maxConcurrencyarg 来运行大型作业。
这通过跨线程有效地拆分数据集来并行化评估。
定义应用程序
首先,我们需要一个应用程序进行评估。让我们为此示例创建一个简单的毒性分类器。
- 蟒
- TypeScript (类型脚本)
from langsmith import traceable, wrappers
from openai import OpenAI
# Optionally wrap the OpenAI client to trace all model calls.
oai_client = wrappers.wrap_openai(OpenAI())
# Optionally add the 'traceable' decorator to trace the inputs/outputs of this function.
@traceable
def toxicity_classifier(inputs: dict) -> dict:
instructions = (
"Please review the user query below and determine if it contains any form of toxic behavior, "
"such as insults, threats, or highly negative comments. Respond with 'Toxic' if it does "
"and 'Not toxic' if it doesn't."
)
messages = [
{"role": "system", "content": instructions},
{"role": "user", "content": inputs["text"]},
]
result = oai_client.chat.completions.create(
messages=messages, model="gpt-4o-mini", temperature=0
)
return {"class": result.choices[0].message.content}
import { OpenAI } from "openai";
import { wrapOpenAI } from "langsmith/wrappers";
import { traceable } from "langsmith/traceable";
// Optionally wrap the OpenAI client to trace all model calls.
const oaiClient = wrapOpenAI(new OpenAI());
// Optionally add the 'traceable' wrapper to trace the inputs/outputs of this function.
const toxicityClassifier = traceable(
async (text: string) => {
const result = await oaiClient.chat.completions.create({
messages: [
{
role: "system",
content: "Please review the user query below and determine if it contains any form of toxic behavior, such as insults, threats, or highly negative comments. Respond with 'Toxic' if it does, and 'Not toxic' if it doesn't.",
},
{ role: "user", content: text },
],
model: "gpt-4o-mini",
temperature: 0,
});
return result.choices[0].message.content;
},
{ name: "toxicityClassifier" }
);
我们可选择启用跟踪来捕获管道中每个步骤的输入和输出。 要了解如何对代码进行注释以进行跟踪,请参阅本指南。
创建或选择数据集
我们需要一个 Dataset 来评估我们的应用程序。我们的数据集将包含带标签的有毒和非有毒文本示例。
- 蟒
- TypeScript (类型脚本)
需要langsmith>=0.3.13
from langsmith import Client
ls_client = Client()
examples = [
{
"inputs": {"text": "Shut up, idiot"},
"outputs": {"label": "Toxic"},
},
{
"inputs": {"text": "You're a wonderful person"},
"outputs": {"label": "Not toxic"},
},
{
"inputs": {"text": "This is the worst thing ever"},
"outputs": {"label": "Toxic"},
},
{
"inputs": {"text": "I had a great day today"},
"outputs": {"label": "Not toxic"},
},
{
"inputs": {"text": "Nobody likes you"},
"outputs": {"label": "Toxic"},
},
{
"inputs": {"text": "This is unacceptable. I want to speak to the manager."},
"outputs": {"label": "Not toxic"},
},
]
dataset = ls_client.create_dataset(dataset_name="Toxic Queries")
ls_client.create_examples(
dataset_id=dataset.id,
examples=examples,
)
import { Client } from "langsmith";
const langsmith = new Client();
// create a dataset
const labeledTexts = [
["Shut up, idiot", "Toxic"],
["You're a wonderful person", "Not toxic"],
["This is the worst thing ever", "Toxic"],
["I had a great day today", "Not toxic"],
["Nobody likes you", "Toxic"],
["This is unacceptable. I want to speak to the manager.", "Not toxic"],
];
const [inputs, outputs] = labeledTexts.reduce<
[Array<{ input: string }>, Array<{ outputs: string }>]
>(
([inputs, outputs], item) => [
[...inputs, { input: item[0] }],
[...outputs, { outputs: item[1] }],
],
[[], []]
);
const datasetName = "Toxic Queries";
const toxicDataset = await langsmith.createDataset(datasetName);
await langsmith.createExamples({ inputs, outputs, datasetId: toxicDataset.id });
有关数据集管理的更多信息,请参阅此处。
定义赋值器
您还可以查看 LangChain 的开源评估包 openevals,了解常见的预构建评估器。
Evaluators 是用于对应用程序输出进行评分的函数。它们采用示例 inputs、实际 outputs,以及 reference outputs(如果存在)。 由于我们有此任务的标签,因此我们的评估器可以直接检查实际输出是否与参考输出匹配。
- 蟒
- TypeScript (类型脚本)
需要langsmith>=0.3.13
def correct(inputs: dict, outputs: dict, reference_outputs: dict) -> bool:
return outputs["class"] == reference_outputs["label"]
Requires langsmith>=0.2.9
import type { EvaluationResult } from "langsmith/evaluation";
function correct({
outputs,
referenceOutputs,
}: {
outputs: Record<string, any>;
referenceOutputs?: Record<string, any>;
}): EvaluationResult {
const score = outputs.output === referenceOutputs?.outputs;
return { key: "correct", score };
}
有关如何定义赋值器的更多信息,请参阅此处。
运行评估
我们将使用 evaluate() / aevaluate() 方法来运行评估。
关键参数是:
- 一个 Target 函数,它接受一个输入字典并返回一个输出字典。这
example.inputsfield 是传递给目标函数的内容。在这种情况下,我们的toxicity_classifier已经设置为接受示例输入,因此我们可以直接使用它。 data- 要评估的 LangSmith 数据集的名称或 UUID,或示例的迭代器evaluators- 用于对函数的输出进行评分的评估器列表
- 蟒
- TypeScript (类型脚本)
需要langsmith>=0.3.13
# Can equivalently use the 'evaluate' function directly:
# from langsmith import evaluate; evaluate(...)
results = ls_client.evaluate(
toxicity_classifier,
data=dataset.name,
evaluators=[correct],
experiment_prefix="gpt-4o-mini, baseline", # optional, experiment name prefix
description="Testing the baseline system.", # optional, experiment description
max_concurrency=4, # optional, add concurrency
)
import { evaluate } from "langsmith/evaluation";
await evaluate((inputs) => toxicityClassifier(inputs["input"]), {
data: datasetName,
evaluators: [correct],
experimentPrefix: "gpt-4o-mini, baseline", // optional, experiment name prefix
maxConcurrency: 4, // optional, add concurrency
});
请参阅此处了解启动评估的其他方法,并在此处了解如何配置评估作业。
探索结果
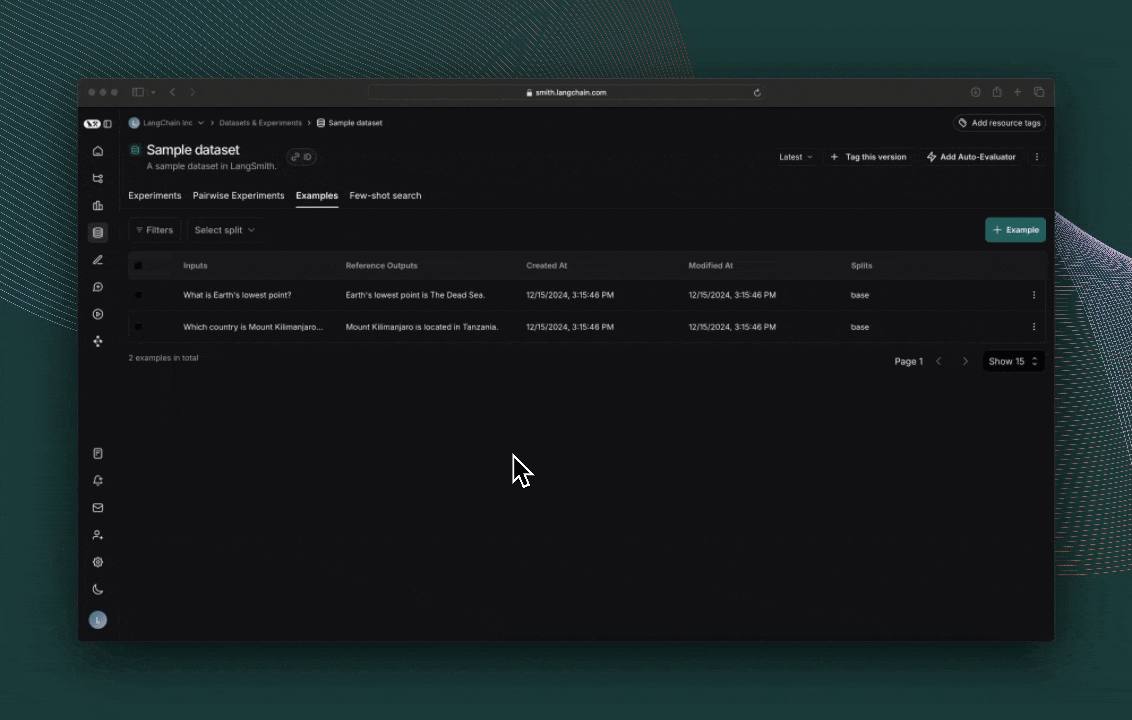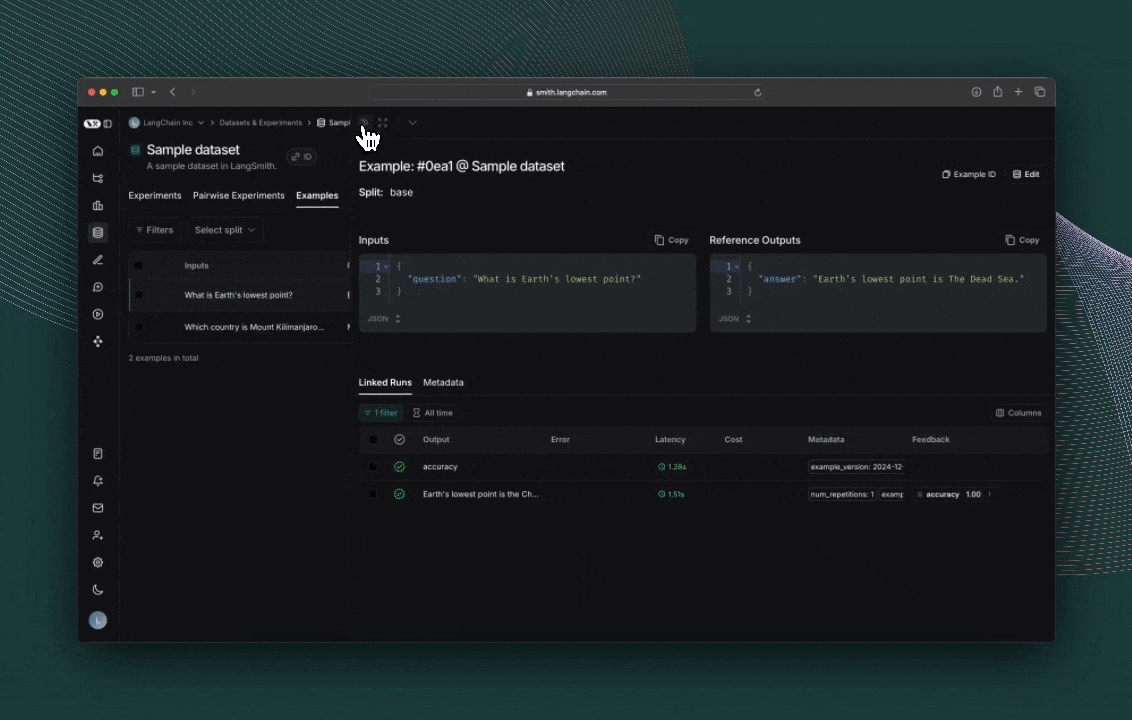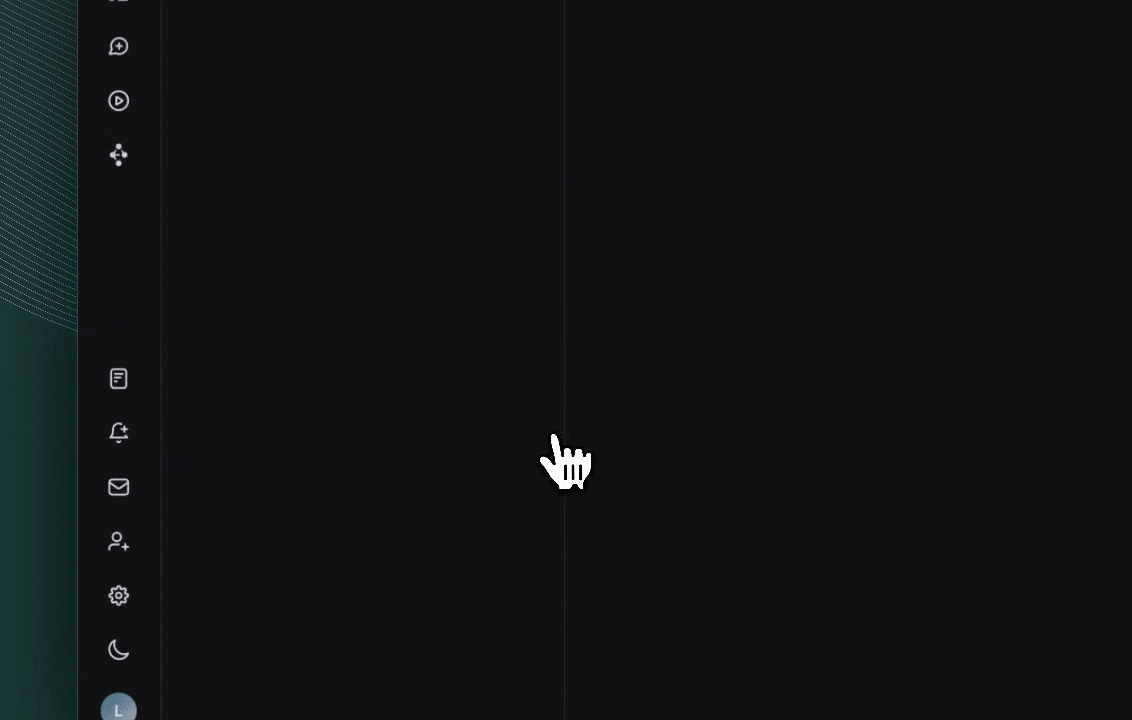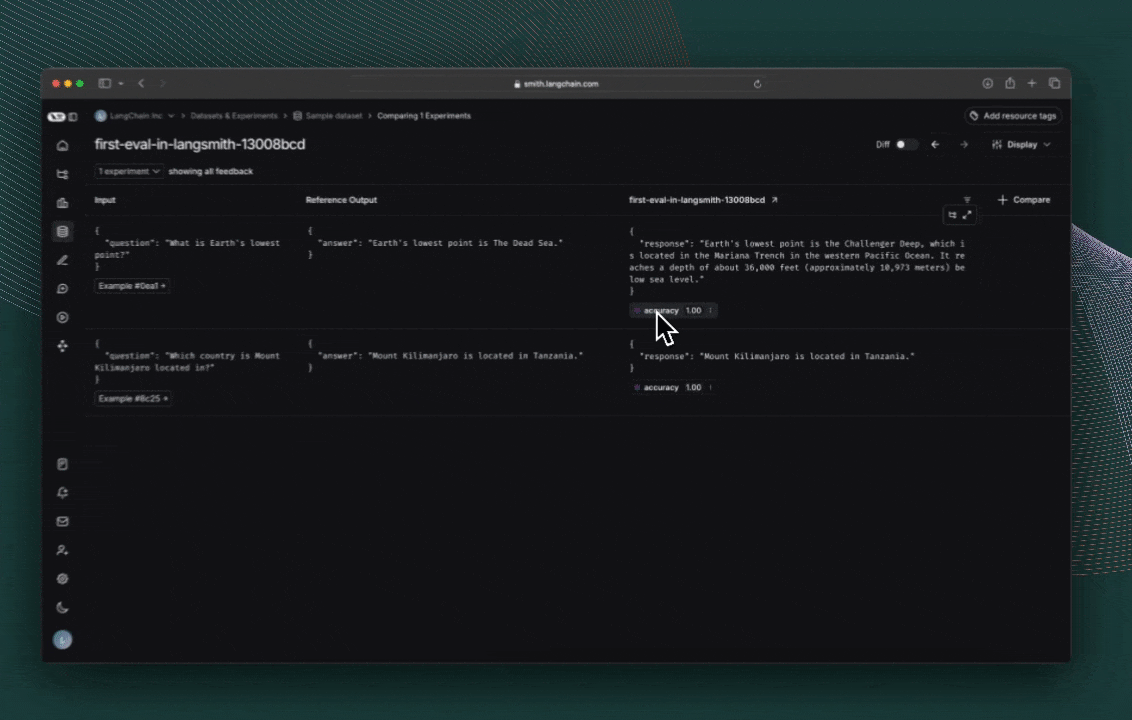
每次调用evaluate()创建一个 Experiment,该 Experiment 可以在 LangSmith UI 中查看或通过 SDK 查询。
评估分数将作为反馈存储在每个实际输出中。
如果已对代码进行注释以进行跟踪,则可以在侧面板视图中打开每行的跟踪。
参考代码
单击可查看合并的代码片段
- 蟒
- TypeScript (类型脚本)
需要langsmith>=0.3.13
from langsmith import Client, traceable, wrappers
from openai import OpenAI
# Step 1. Define an application
oai_client = wrappers.wrap_openai(OpenAI())
@traceable
def toxicity_classifier(inputs: dict) -> str:
system = (
"Please review the user query below and determine if it contains any form of toxic behavior, "
"such as insults, threats, or highly negative comments. Respond with 'Toxic' if it does "
"and 'Not toxic' if it doesn't."
)
messages = [
{"role": "system", "content": system},
{"role": "user", "content": inputs["text"]},
]
result = oai_client.chat.completions.create(
messages=messages, model="gpt-4o-mini", temperature=0
)
return result.choices[0].message.content
# Step 2. Create a dataset
ls_client = Client()
dataset = ls_client.create_dataset(dataset_name="Toxic Queries")
examples = [
{
"inputs": {"text": "Shut up, idiot"},
"outputs": {"label": "Toxic"},
},
{
"inputs": {"text": "You're a wonderful person"},
"outputs": {"label": "Not toxic"},
},
{
"inputs": {"text": "This is the worst thing ever"},
"outputs": {"label": "Toxic"},
},
{
"inputs": {"text": "I had a great day today"},
"outputs": {"label": "Not toxic"},
},
{
"inputs": {"text": "Nobody likes you"},
"outputs": {"label": "Toxic"},
},
{
"inputs": {"text": "This is unacceptable. I want to speak to the manager."},
"outputs": {"label": "Not toxic"},
},
]
ls_client.create_examples(
dataset_id=dataset.id,
examples=examples,
)
# Step 3. Define an evaluator
def correct(inputs: dict, outputs: dict, reference_outputs: dict) -> bool:
return outputs["output"] == reference_outputs["label"]
# Step 4. Run the evaluation
# Client.evaluate() and evaluate() behave the same.
results = ls_client.evaluate(
toxicity_classifier,
data=dataset.name,
evaluators=[correct],
experiment_prefix="gpt-4o-mini, simple", # optional, experiment name prefix
description="Testing the baseline system.", # optional, experiment description
max_concurrency=4, # optional, add concurrency
)
import { OpenAI } from "openai";
import { Client } from "langsmith";
import { evaluate, EvaluationResult } from "langsmith/evaluation";
import type { Run, Example } from "langsmith/schemas";
import { traceable } from "langsmith/traceable";
import { wrapOpenAI } from "langsmith/wrappers";
const oaiClient = wrapOpenAI(new OpenAI());
const toxicityClassifier = traceable(
async (text: string) => {
const result = await oaiClient.chat.completions.create({
messages: [
{
role: "system",
content: "Please review the user query below and determine if it contains any form of toxic behavior, such as insults, threats, or highly negative comments. Respond with 'Toxic' if it does, and 'Not toxic' if it doesn't.",
},
{ role: "user", content: text },
],
model: "gpt-4o-mini",
temperature: 0,
});
return result.choices[0].message.content;
},
{ name: "toxicityClassifier" }
);
const langsmith = new Client();
// create a dataset
const labeledTexts = [
["Shut up, idiot", "Toxic"],
["You're a wonderful person", "Not toxic"],
["This is the worst thing ever", "Toxic"],
["I had a great day today", "Not toxic"],
["Nobody likes you", "Toxic"],
["This is unacceptable. I want to speak to the manager.", "Not toxic"],
];
const [inputs, outputs] = labeledTexts.reduce<
[Array<{ input: string }>, Array<{ outputs: string }>]
>(
([inputs, outputs], item) => [
[...inputs, { input: item[0] }],
[...outputs, { outputs: item[1] }],
],
[[], []]
);
const datasetName = "Toxic Queries";
const toxicDataset = await langsmith.createDataset(datasetName);
await langsmith.createExamples({ inputs, outputs, datasetId: toxicDataset.id });
// Row-level evaluator
function correct({
outputs,
referenceOutputs,
}: {
outputs: Record<string, any>;
referenceOutputs?: Record<string, any>;
}): EvaluationResult {
const score = outputs.output === referenceOutputs?.outputs;
return { key: "correct", score };
}
await evaluate((inputs) => toxicityClassifier(inputs["input"]), {
data: datasetName,
evaluators: [correct],
experimentPrefix: "gpt-4o-mini, simple", // optional, experiment name prefix
maxConcurrency: 4, // optional, add concurrency
});