使用 LangSmith 运行 SWE-bench
SWE-bench 是开发人员测试其编码代理的最流行(也是最困难)的基准测试之一。在本演练中,我们将向您展示如何将 SWE-bench 数据集加载到 LangSmith 中并轻松在其上运行评估,从而让您能够更好地了解代理行为,而不是使用现成的 SWE-bench 评估套件。这使您可以更快地固定特定问题并快速迭代您的代理以提高性能!
加载数据
为了加载数据,我们将拉取dev从 Hugging Face 中分离出来,但对于您的用例,您可能希望提取其中一个test或trainsplits 的 API,如果您想合并多个 split,您可以使用pd.concat.
import pandas as pd
splits = {'dev': 'data/dev-00000-of-00001.parquet', 'test': 'data/test-00000-of-00001.parquet', 'train': 'data/train-00000-of-00001.parquet'}
df = pd.read_parquet("hf://datasets/princeton-nlp/SWE-bench/" + splits["dev"])
编辑 'version' 列
这是非常重要的一步!如果您跳过,代码的其余部分将不起作用!
这version列包含所有字符串值,但所有值都采用浮点格式,因此当您上传 CSV 以创建 LangSmith 数据集时,它们会转换为浮点数。尽管您可以在实验期间将值转换为字符串,但问题会出现在"0.10".当转换为 float 时,您将获得 value0.1,这将变为"0.1"如果您将其转换为字符串 - 在执行建议的补丁期间导致 Key 错误。
为了解决这个问题,我们需要 LangSmith 停止尝试将versioncolumn 设置为 floats。为了做到这一点,我们可以为每个它们附加一个不兼容的字符串前缀。然后,我们需要在进行评估时对这个前缀进行拆分,以获得实际的version价值。我们在这里选择的前缀是字符串"version:".
将来将添加在将 CSV 上传到 LangSmith 时选择列类型的功能,以避免使用此解决方法。
df['version'] = df['version'].apply(lambda x: f"version:{x}")
将数据上传到 LangSmith
保存为 CSV
要将数据上传到 LangSmith,我们首先需要将其保存为 CSV,我们可以使用to_csvpandas 提供的函数。确保将此文件保存在您容易访问的位置。
df.to_csv("./../SWE-bench.csv",index=False)
手动将 CSV 上传到 LangSmith
现在,我们已准备好将 CSV 上传到 LangSmith。进入 LangSmith 网站 (smith.langchain.com) 后,转到Datasets & Testing选项卡,然后单击+ New Dataset按钮。
然后单击Upload CSV按钮,然后选择您在上一步中保存的 CSV 文件。然后,您可以为数据集指定名称和描述。
接下来,选择Key-Value作为数据集类型。最后前往Create Schema部分,并将 ALL OF THE KEYS 添加为Input fields.没有Output fields在此示例中,因为我们的评估器不是与引用进行比较,而是在 Docker 容器中运行实验的输出,以确保代码实际解决 PR 问题。
填充Input fields(并留下了Output fields空的!您可以单击蓝色的Create按钮,您的数据集将被创建!
以编程方式将 CSV 上传到 LangSmith
或者,您也可以使用 sdk 将 csv 上传到 LangSmith,如下面的代码块所示:
dataset = client.upload_csv(
csv_file="./../SWE-bench-dev.csv",
input_keys=list(df.columns),
output_keys=[],
name="swe-bench-programatic-upload",
description="SWE-bench dataset",
data_type="kv"
)
创建数据集拆分以加快测试
由于在所有示例上运行 SWE-bench 评估器需要很长时间,因此您可以创建一个“测试”拆分,以便快速测试评估器和您的代码。阅读本指南以了解有关管理数据集拆分的更多信息,或观看此简短视频,了解如何执行此作(要访问视频的起始页,只需单击上面创建的数据集,然后转到Examples选项卡):
运行我们的预测函数
在 SWE-bench 上运行评估的工作方式与您通常在 LangSmith 上运行的大多数评估略有不同,因为我们没有参考输出。因此,我们首先在不运行计算器的情况下生成所有输出(请注意evaluatecall 没有evaluators参数集)。在本例中,我们返回了一个虚拟 predict 函数,但您可以将代理逻辑插入predict功能使其按预期工作。
from langsmith import evaluate
from langsmith import Client
client = Client()
def predict(inputs: dict):
return {"instance_id":inputs['instance_id'],"model_patch":"None","model_name_or_path":"test-model"}
result = evaluate(
predict,
data=client.list_examples(dataset_id="a9bffcdf-1dfe-4aef-8805-8806f0110067",splits=["test"]),
)
在以下位置查看实验 'perfect-lip-22' 的评估结果: https://smith.langchain.com/o/ebbaf2eb-769b-4505-aca2-d11de10372a4/datasets/a9bffcdf-1dfe-4aef-8805-8806f0110067/compare?selectedSessions=182de5dc-fc9d-4065-a3e1-34527f952fd8
3 小时 [00:00, 24.48 小时/秒]
使用 SWE-bench 评估我们的预测
现在我们可以运行以下代码来运行我们在 Docker 中生成的预测补丁。此代码从SWE-bench run_evaluation.py 文件。
基本上,该代码将 docker 镜像设置为并行运行预测,这大大减少了评估所需的时间。此屏幕截图解释了如何SWE-bench在后台进行评估。要全面理解它,请务必通读 GitHub 存储库中的代码。
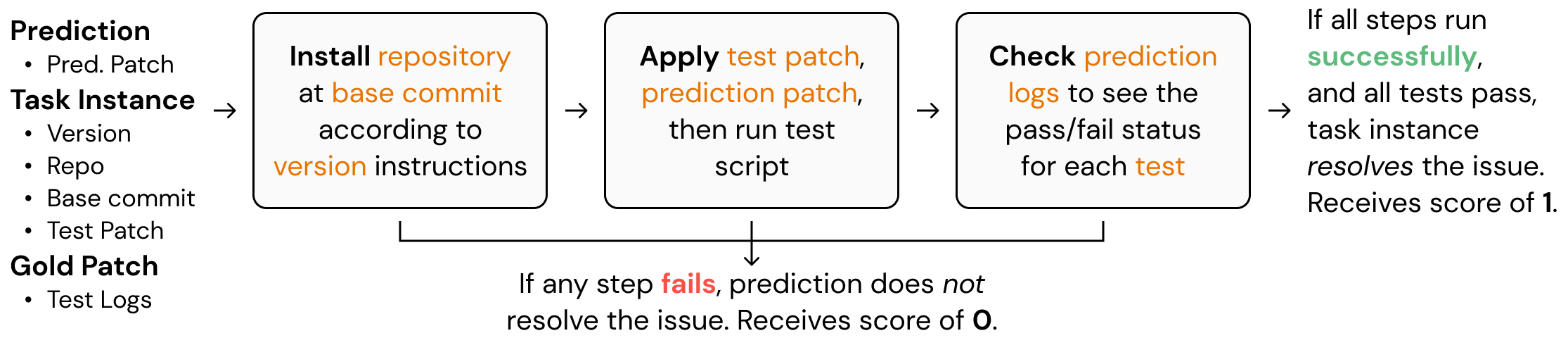
函数convert_runs_to_langsmith_feedback将 docker 文件生成的日志转换为一个不错的 .json 文件,其中包含 LangSmith 的典型 key/score 方法中的反馈。
from swebench.harness.run_evaluation import run_instances
import resource
import docker
from swebench.harness.docker_utils import list_images, clean_images
from swebench.harness.docker_build import build_env_images
from pathlib import Path
import json
import os
RUN_EVALUATION_LOG_DIR = Path("logs/run_evaluation")
LANGSMITH_EVALUATION_DIR = './langsmith_feedback/feedback.json'
def convert_runs_to_langsmith_feedback(
predictions: dict,
full_dataset: list,
run_id: str
) -> float:
"""
Convert logs from docker containers into LangSmith feedback.
Args:
predictions (dict): Predictions dict generated by the model
full_dataset (list): List of all instances
run_id (str): Run ID
"""
feedback_for_all_instances = {}
for instance in full_dataset:
feedback_for_instance = []
instance_id = instance['instance_id']
prediction = predictions[instance_id]
if prediction.get("model_patch", None) in ["", None]:
# Prediction returned an empty patch
feedback_for_all_instances[prediction['run_id']] = [{"key":"non-empty-patch","score":0},
{"key":"completed-patch","score":0},
{"key":"resolved-patch","score":0}]
continue
feedback_for_instance.append({"key":"non-empty-patch","score":1})
report_file = (
RUN_EVALUATION_LOG_DIR
/ run_id
/ prediction["model_name_or_path"].replace("/", "__")
/ prediction['instance_id']
/ "report.json"
)
if report_file.exists():
# If report file exists, then the instance has been run
feedback_for_instance.append({"key":"completed-patch","score":1})
report = json.loads(report_file.read_text())
# Check if instance actually resolved the PR
if report[instance_id]["resolved"]:
feedback_for_instance.append({"key":"resolved-patch","score":1})
else:
feedback_for_instance.append({"key":"resolved-patch","score":0})
else:
# The instance did not run successfully
feedback_for_instance += [{"key":"completed-patch","score":0},{"key":"resolved-patch","score":0}]
feedback_for_all_instances[prediction['run_id']] = feedback_for_instance
os.makedirs(os.path.dirname(LANGSMITH_EVALUATION_DIR), exist_ok=True)
with open(LANGSMITH_EVALUATION_DIR, 'w') as json_file:
json.dump(feedback_for_all_instances, json_file)
def evaluate_predictions(
dataset: list,
predictions: list,
max_workers: int,
force_rebuild: bool,
cache_level: str,
clean: bool,
open_file_limit: int,
run_id: str,
timeout: int,
):
"""
Run evaluation harness for the given dataset and predictions.
"""
# set open file limit
assert len(run_id) > 0, "Run ID must be provided"
resource.setrlimit(resource.RLIMIT_NOFILE, (open_file_limit, open_file_limit))
client = docker.from_env()
existing_images = list_images(client)
print(f"Running {len(dataset)} unevaluated instances...")
# build environment images + run instances
build_env_images(client, dataset, force_rebuild, max_workers)
run_instances(predictions, dataset, cache_level, clean, force_rebuild, max_workers, run_id, timeout)
# clean images + make final report
clean_images(client, existing_images, cache_level, clean)
convert_runs_to_langsmith_feedback(predictions,dataset,run_id)
dataset = []
predictions = {}
for res in result:
predictions[res['run'].outputs['instance_id']] = {**res['run'].outputs,**{"run_id":str(res['run'].id)}}
dataset.append(res['run'].inputs['inputs'])
for d in dataset:
d['version'] = d['version'].split(":")[1]
evaluate_predictions(dataset,predictions,max_workers=8,force_rebuild=False,cache_level="env",clean=False \
,open_file_limit=4096,run_id="test",timeout=1_800)
Running 3 unevaluated instances...
Base image sweb.base.arm64:latest already exists, skipping build.
Base images built successfully.
Total environment images to build: 2
Building environment images: 100%|██████████| 2/2 [00:47<00:00, 23.94s/it]
All environment images built successfully.
Running 3 instances...
0%| | 0/3 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
Evaluation error for sqlfluff__sqlfluff-884: >>>>> Patch Apply Failed:
patch unexpectedly ends in middle of line
patch: **** Only garbage was found in the patch input.
Check (logs/run_evaluation/test/test-model/sqlfluff__sqlfluff-884/run_instance.log) for more information.
Evaluation error for sqlfluff__sqlfluff-4151: >>>>> Patch Apply Failed:
patch unexpectedly ends in middle of line
patch: **** Only garbage was found in the patch input.
Check (logs/run_evaluation/test/test-model/sqlfluff__sqlfluff-4151/run_instance.log) for more information.
Evaluation error for sqlfluff__sqlfluff-2849: >>>>> Patch Apply Failed:
patch: **** Only garbage was found in the patch input.
patch unexpectedly ends in middle of line
Check (logs/run_evaluation/test/test-model/sqlfluff__sqlfluff-2849/run_instance.log) for more information.
100%|██████████| 3/3 [00:30<00:00, 10.04s/it]
All instances run.
Cleaning cached images...
Removed 0 images.
将评估发送给 LangSmith
现在,我们实际上可以使用evaluate_existing功能。在这种情况下,我们的 evaluate 函数非常简单,因为convert_runs_to_langsmith_feedback功能将所有反馈保存到一个文件中,使我们的生活变得非常轻松。
from langsmith import evaluate_existing
from langsmith.schemas import Example, Run
def swe_bench_evaluator(run: Run, example: Example):
with open(LANGSMITH_EVALUATION_DIR, 'r') as json_file:
langsmith_eval = json.load(json_file)
return {"results": langsmith_eval[str(run.id)]}
experiment_name = result.experiment_name
evaluate_existing(experiment_name, evaluators=[swe_bench_evaluator])
View the evaluation results for experiment: 'perfect-lip-22' at:
https://smith.langchain.com/o/ebbaf2eb-769b-4505-aca2-d11de10372a4/datasets/a9bffcdf-1dfe-4aef-8805-8806f0110067/compare?selectedSessions=182de5dc-fc9d-4065-a3e1-34527f952fd8
3it [00:01, 1.52it/s]
<ExperimentResults perfect-lip-22>
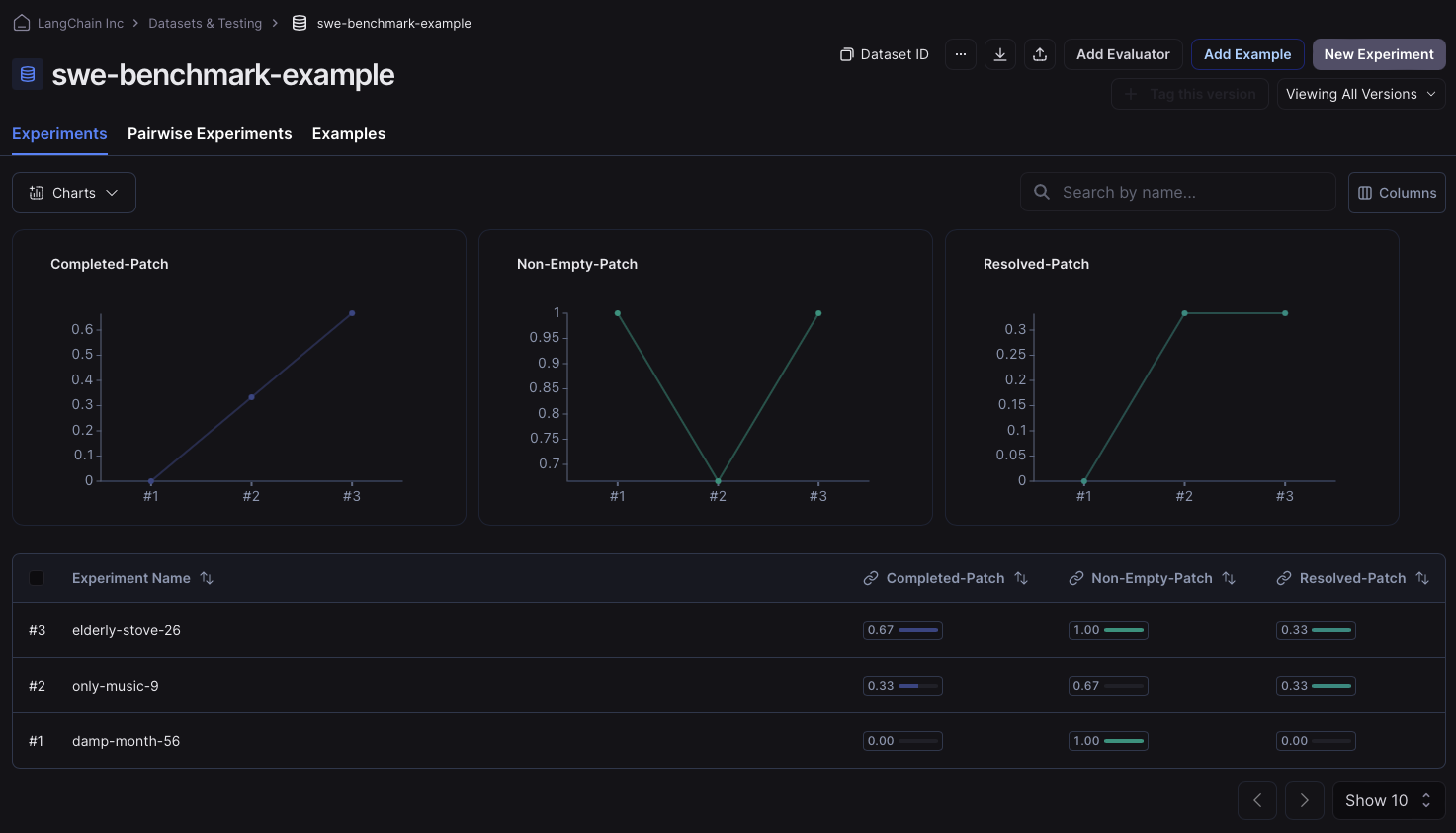
运行后,我们可以转到数据集的 experiments 选项卡,并检查我们的反馈密钥是否已正确分配。如果是,您应该会看到类似于下图的内容: