注释代码以进行跟踪
如果您决定不再跟踪运行,则可以删除LANGSMITH_TRACING环境变量。
请注意,这不会影响RunTree对象或 API 用户,因为这些是低级的,不受跟踪切换的影响。
有几种方法可以记录对 LangSmith 的跟踪。
如果您使用的是 LangChain(Python 或 JS/TS),则可以跳过此部分,直接转到特定于 LangChain 的说明。
用@traceable / traceable
LangSmith 使用@traceabledecorator 和traceable函数。
- 蟒
- TypeScript (类型脚本)
这@traceabledecorator 是一种记录来自 LangSmith Python SDK 的跟踪的简单方法。只需用@traceable.
from langsmith import traceable
from openai import Client
openai = Client()
@traceable
def format_prompt(subject):
return [
{
"role": "system",
"content": "You are a helpful assistant.",
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": f"What's a good name for a store that sells {subject}?"
}
]
@traceable(run_type="llm")
def invoke_llm(messages):
return openai.chat.completions.create(
messages=messages, model="gpt-4o-mini", temperature=0
)
@traceable
def parse_output(response):
return response.choices[0].message.content
@traceable
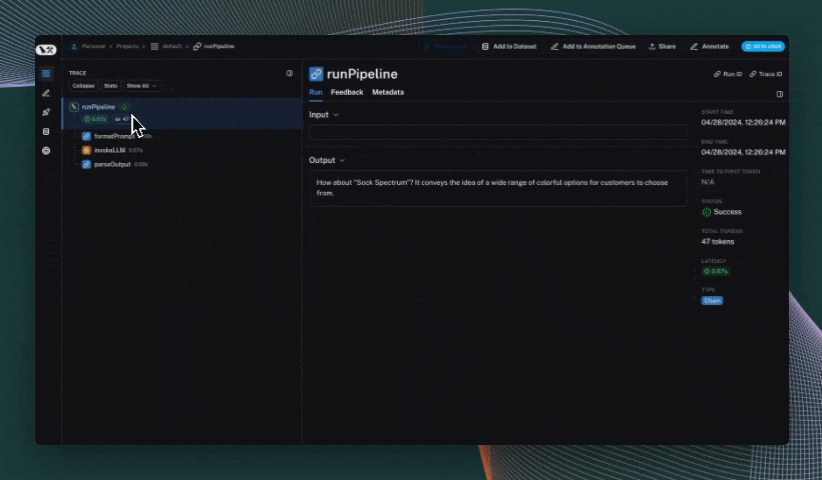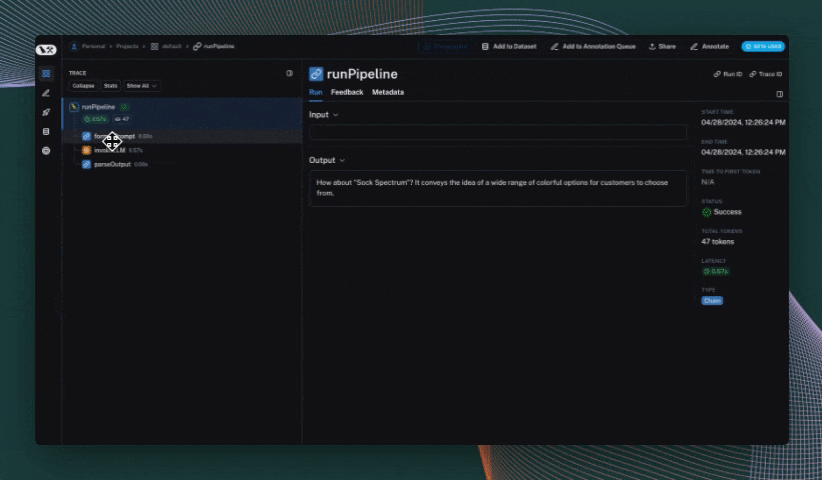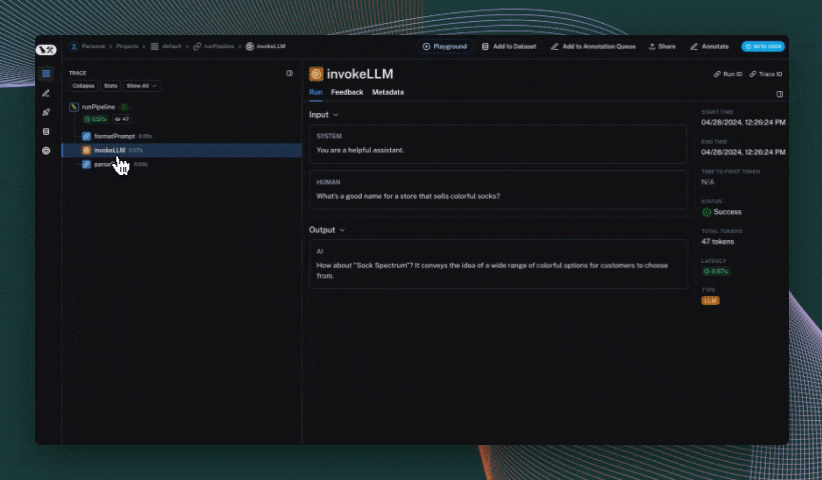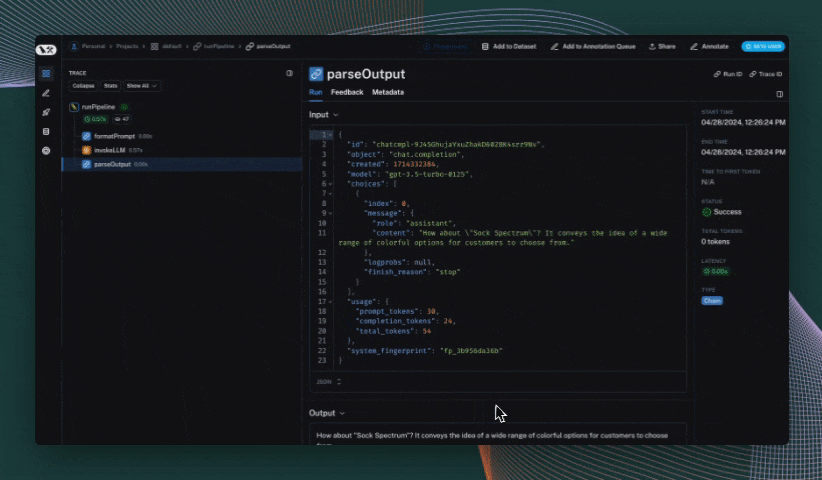
def run_pipeline():
messages = format_prompt("colorful socks")
response = invoke_llm(messages)
return parse_output(response)
run_pipeline()
The traceable function is a simple way to log traces from the LangSmith TypeScript SDK. Simply wrap any function with traceable.
Note that when wrapping a sync function with traceable, (e.g. formatPrompt in the example below), you should use the await keyword when calling it to ensure the trace is logged correctly.
import { traceable } from "langsmith/traceable";
import OpenAI from "openai";
const openai = new OpenAI();
const formatPrompt = traceable(
(subject: string) => {
return [
{
role: "system" as const,
content: "You are a helpful assistant.",
},
{
role: "user" as const,
content: `What's a good name for a store that sells ${subject}?`,
},
];
},
{ name: "formatPrompt" }
);
const invokeLLM = traceable(
async ({ messages }: { messages: { role: string; content: string }[] }) => {
return openai.chat.completions.create({
model: "gpt-4o-mini",
messages: messages,
temperature: 0,
});
},
{ run_type: "llm", name: "invokeLLM" }
);
const parseOutput = traceable(
(response: any) => {
return response.choices[0].message.content;
},
{ name: "parseOutput" }
);
const runPipeline = traceable(
async () => {
const messages = await formatPrompt("colorful socks");
const response = await invokeLLM({ messages });
return parseOutput(response);
},
{ name: "runPipeline" }
);
await runPipeline();
使用trace上下文管理器 (仅限 Python)
在 Python 中,您可以使用tracecontext manager 将跟踪记录到 LangSmith。这在以下情况下非常有用:
- 您希望记录特定代码块的跟踪。
- 您希望控制跟踪的输入、输出和其他属性。
- 使用 decorator 或 wrapper 是不可行的。
- 以上任何或全部。
上下文管理器与traceabledecorator 和wrap_openaiwrapper 中,以便您可以在同一应用程序中一起使用它们。
import openai
import langsmith as ls
from langsmith.wrappers import wrap_openai
client = wrap_openai(openai.Client())
@ls.traceable(run_type="tool", name="Retrieve Context")
def my_tool(question: str) -> str:
return "During this morning's meeting, we solved all world conflict."
def chat_pipeline(question: str):
context = my_tool(question)
messages = [
{ "role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant. Please respond to the user's request only based on the given context." },
{ "role": "user", "content": f"Question: {question}\nContext: {context}"}
]
chat_completion = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o-mini", messages=messages
)
return chat_completion.choices[0].message.content
app_inputs = {"input": "Can you summarize this morning's meetings?"}
with ls.trace("Chat Pipeline", "chain", project_name="my_test", inputs=app_inputs) as rt:
output = chat_pipeline("Can you summarize this morning's meetings?")
rt.end(outputs={"output": output})
包装 OpenAI 客户端
这wrap_openai/wrapOpenAIPython/TypeScript 中的方法允许您包装 OpenAI 客户端以自动记录跟踪 - 无需装饰器或函数包装!
包装器与@traceabledecorator 或traceable功能,并且可以在同一应用程序中同时使用两者。
工具调用会自动呈现
- 蟒
- TypeScript (类型脚本)
import openai
from langsmith import traceable
from langsmith.wrappers import wrap_openai
client = wrap_openai(openai.Client())
@traceable(run_type="tool", name="Retrieve Context")
def my_tool(question: str) -> str:
return "During this morning's meeting, we solved all world conflict."
@traceable(name="Chat Pipeline")
def chat_pipeline(question: str):
context = my_tool(question)
messages = [
{ "role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant. Please respond to the user's request only based on the given context." },
{ "role": "user", "content": f"Question: {question}\nContext: {context}"}
]
chat_completion = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o-mini", messages=messages
)
return chat_completion.choices[0].message.content
chat_pipeline("Can you summarize this morning's meetings?")
import OpenAI from "openai";
import { traceable } from "langsmith/traceable";
import { wrapOpenAI } from "langsmith/wrappers";
const client = wrapOpenAI(new OpenAI());
const myTool = traceable(async (question: string) => {
return "During this morning's meeting, we solved all world conflict.";
}, { name: "Retrieve Context", run_type: "tool" });
const chatPipeline = traceable(async (question: string) => {
const context = await myTool(question);
const messages = [
{
role: "system",
content:
"You are a helpful assistant. Please respond to the user's request only based on the given context.",
},
{ role: "user", content: `Question: ${question} Context: ${context}` },
];
const chatCompletion = await client.chat.completions.create({
model: "gpt-4o-mini",
messages: messages,
});
return chatCompletion.choices[0].message.content;
}, { name: "Chat Pipeline" });
await chatPipeline("Can you summarize this morning's meetings?");
使用RunTree应用程序接口
另一种更明确的记录 LangSmith 跟踪的方法是通过RunTree应用程序接口。此 API 允许您更好地控制跟踪 - 您可以手动
创建 RUNS 和 CHILDREN RUNS 来组合跟踪。您仍然需要将LANGSMITH_API_KEY但LANGSMITH_TRACING莫
对于此方法是必需的。
不建议使用此方法,因为在传播跟踪上下文时更容易出错。
- 蟒
- TypeScript (类型脚本)
import openai
from langsmith.run_trees import RunTree
# This can be a user input to your app
question = "Can you summarize this morning's meetings?"
# Create a top-level run
pipeline = RunTree(
name="Chat Pipeline",
run_type="chain",
inputs={"question": question}
)
pipeline.post()
# This can be retrieved in a retrieval step
context = "During this morning's meeting, we solved all world conflict."
messages = [
{ "role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant. Please respond to the user's request only based on the given context." },
{ "role": "user", "content": f"Question: {question}\nContext: {context}"}
]
# Create a child run
child_llm_run = pipeline.create_child(
name="OpenAI Call",
run_type="llm",
inputs={"messages": messages},
)
child_llm_run.post()
# Generate a completion
client = openai.Client()
chat_completion = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o-mini", messages=messages
)
# End the runs and log them
child_llm_run.end(outputs=chat_completion)
child_llm_run.patch()
pipeline.end(outputs={"answer": chat_completion.choices[0].message.content})
pipeline.patch()
import OpenAI from "openai";
import { RunTree } from "langsmith";
// This can be a user input to your app
const question = "Can you summarize this morning's meetings?";
const pipeline = new RunTree({
name: "Chat Pipeline",
run_type: "chain",
inputs: { question }
});
await pipeline.postRun();
// This can be retrieved in a retrieval step
const context = "During this morning's meeting, we solved all world conflict.";
const messages = [
{ role: "system", content: "You are a helpful assistant. Please respond to the user's request only based on the given context." },
{ role: "user", content: `Question: ${question}
Context: ${context}` }
];
// Create a child run
const childRun = await pipeline.createChild({
name: "OpenAI Call",
run_type: "llm",
inputs: { messages },
});
await childRun.postRun();
// Generate a completion
const client = new OpenAI();
const chatCompletion = await client.chat.completions.create({
model: "gpt-4o-mini",
messages: messages,
});
// End the runs and log them
childRun.end(chatCompletion);
await childRun.patchRun();
pipeline.end({ outputs: { answer: chatCompletion.choices[0].message.content } });
await pipeline.patchRun();
用法示例
您可以扩展上面的实用程序以方便地跟踪任何代码。以下是一些示例扩展:
跟踪类中的任何公共方法:
from typing import Any, Callable, Type, TypeVar
T = TypeVar("T")
def traceable_cls(cls: Type[T]) -> Type[T]:
"""Instrument all public methods in a class."""
def wrap_method(name: str, method: Any) -> Any:
if callable(method) and not name.startswith("__"):
return traceable(name=f"{cls.__name__}.{name}")(method)
return method
# Handle __dict__ case
for name in dir(cls):
if not name.startswith("_"):
try:
method = getattr(cls, name)
setattr(cls, name, wrap_method(name, method))
except AttributeError:
# Skip attributes that can't be set (e.g., some descriptors)
pass
# Handle __slots__ case
if hasattr(cls, "__slots__"):
for slot in cls.__slots__: # type: ignore[attr-defined]
if not slot.startswith("__"):
try:
method = getattr(cls, slot)
setattr(cls, slot, wrap_method(slot, method))
except AttributeError:
# Skip slots that don't have a value yet
pass
return cls
@traceable_cls
class MyClass:
def __init__(self, some_val: int):
self.some_val = some_val
def combine(self, other_val: int):
return self.some_val + other_val
# See trace: https://smith.langchain.com/public/882f9ecf-5057-426a-ae98-0edf84fdcaf9/r
MyClass(13).combine(29)
确保在退出之前提交所有跟踪
LangSmith 的跟踪是在后台线程中完成的,以避免阻碍您的生产应用程序。这意味着您的进程可能会在所有跟踪成功发布到 LangSmith 之前结束。 以下是一些选项,可确保在退出应用程序之前提交所有跟踪。
使用 LangSmith SDK
如果您使用的是独立版 LangSmith 开发工具包,则可以使用flush退出前的方法:
- 蟒
- TypeScript (类型脚本)
from langsmith import Client
client = Client()
@traceable(client=client)
async def my_traced_func():
# Your code here...
pass
try:
await my_traced_func()
finally:
await client.flush()
import { Client } from "langsmith";
const langsmithClient = new Client({});
const myTracedFunc = traceable(
async () => {
// Your code here...
},
{ client: langsmithClient }
);
try {
await myTracedFunc();
} finally {
await langsmithClient.flush();
}
使用 LangChain
如果你使用的是 LangChain,请参考我们的 LangChain 追踪指南。
如果您更喜欢视频教程,请观看 LangSmith 简介课程中的跟踪基础知识视频。