如何使用 pytest 运行评估(测试版)
LangSmith pytest 插件允许 Python 开发人员将其数据集和评估定义为 pytest 测试用例。
与evaluate()evaluation flow,这在以下情况下非常有用:
- 每个示例需要不同的评估逻辑
- 您希望断言二进制期望,并且都在 LangSmith 中跟踪这些断言,并在本地(例如在 CI 管道中)引发断言错误
- 你想要类似 pytest 的终端输出
- 您已经使用 pytest 测试了您的应用程序,并希望添加 LangSmith 跟踪
pytest 集成处于测试阶段,在即将发布的版本中可能会发生变化。
JS/TS SDK 具有类似的 Vitest/Jest 集成。
安装
此功能需要 Python SDK 版本langsmith>=0.3.4.
pip install -U "langsmith[pytest]"
定义和运行测试
pytest 集成允许您将数据集和评估器定义为测试用例。
要在 LangSmith 中跟踪测试,请添加@pytest.mark.langsmith装饰。
每个修饰的测试用例都将同步到数据集示例。
当您运行测试套件时,数据集将更新,并将创建一个新实验,每个测试用例都有一个结果。
###################### my_app/main.py ######################
import openai
from langsmith import traceable, wrappers
oai_client = wrappers.wrap_openai(openai.OpenAI())
@traceable
def generate_sql(user_query: str) -> str:
result = oai_client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o-mini",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": "Convert the user query to a SQL query."},
{"role": "user", "content": user_query},
],
)
return result.choices[0].message.content
###################### tests/test_my_app.py ######################
import pytest
from langsmith import testing as t
def is_valid_sql(query: str) -> bool:
"""Return True if the query is valid SQL."""
return True # Dummy implementation
@pytest.mark.langsmith # <-- Mark as a LangSmith test case
def test_sql_generation_select_all() -> None:
user_query = "Get all users from the customers table"
t.log_inputs({"user_query": user_query}) # <-- Log example inputs, optional
expected = "SELECT * FROM customers;"
t.log_reference_outputs({"sql": expected}) # <-- Log example reference outputs, optional
sql = generate_sql(user_query)
t.log_outputs({"sql": sql}) # <-- Log run outputs, optional
t.log_feedback(key="valid_sql", score=is_valid_sql(sql)) # <-- Log feedback, optional
assert sql == expected # <-- Test pass/fail status automatically logged to LangSmith under 'pass' feedback key
当您运行此测试时,它将具有默认的pass基于测试用例通过/失败的布尔反馈键。
它还将跟踪您记录的任何输入、输出和引用(预期)输出。
用pytest就像您通常运行测试一样:
pytest tests/
在大多数情况下,我们建议设置测试套件名称:
LANGSMITH_TEST_SUITE='SQL app tests' pytest tests/
每次运行此测试套件时,LangSmith 都会:
- 为每个测试文件创建一个数据集。如果此测试文件的数据集已存在,则会更新该数据集
- 在每个创建/更新的数据集中创建实验
- 为每个测试用例创建一个 Experiment 行,其中包含您记录的 inputs、outputs、reference outputs(引用输出)和 feedback(反馈)
- 在
pass每个测试用例的 feedback 键
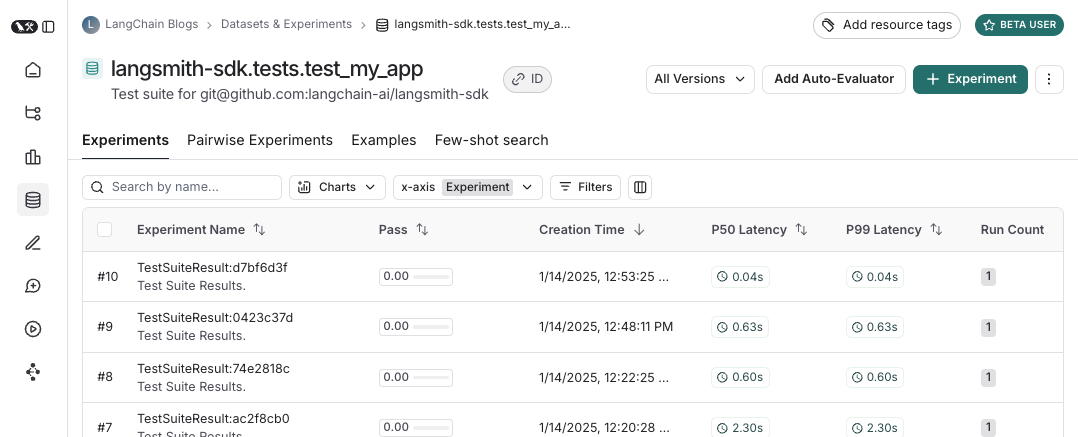
以下是测试套件数据集的样子:
针对该测试套件的实验是什么样的:
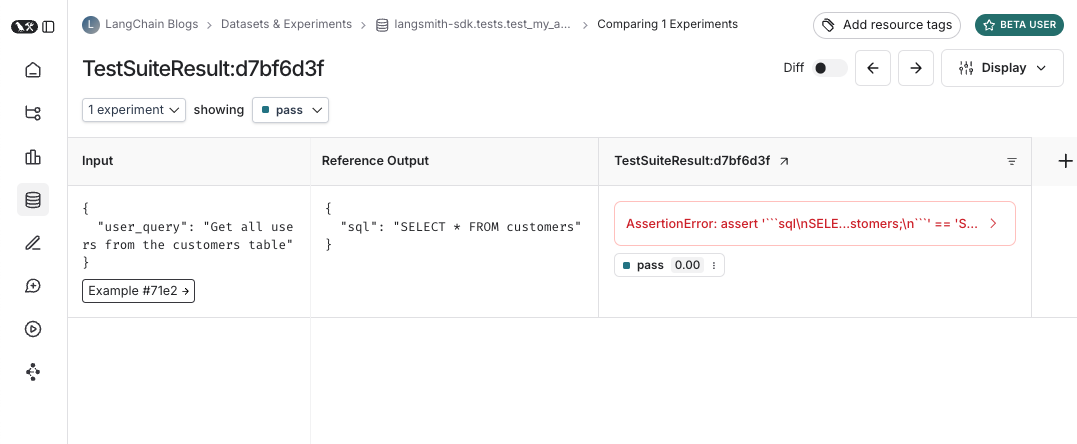
对 Log inputs、output 和 reference output
每次运行测试时,我们都会将其同步到数据集示例,并将其跟踪为运行。
有几种不同的方法可以跟踪示例输入和参考输出以及运行输出。
最简单的方法是使用log_inputs,log_outputs和log_reference_outputs方法。
您可以随时在测试中运行这些来更新示例并为该测试运行:
import pytest
from langsmith import testing as t
@pytest.mark.langsmith
def test_foo() -> None:
t.log_inputs({"a": 1, "b": 2})
t.log_reference_outputs({"foo": "bar"})
t.log_outputs({"foo": "baz"})
assert True
运行此测试将创建/更新名为 “test_foo” 的示例,输入{"a": 1, "b": 2}、参考输出{"foo": "bar"}并使用输出跟踪运行{"foo": "baz"}.
注意:如果运行log_inputs,log_outputs或log_reference_outputs两次,则之前的值将被覆盖。
定义示例输入和引用输出的另一种方法是通过 pytest 夹具/参数化。
默认情况下,测试函数的任何参数都将记录为相应示例的输入。
如果某些参数用于重置引用输出,则可以指定它们应使用@pytest.mark.langsmith(output_keys=["name_of_ref_output_arg"]):
import pytest
@pytest.fixture
def c() -> int:
return 5
@pytest.fixture
def d() -> int:
return 6
@pytest.mark.langsmith(output_keys=["d"])
def test_cd(c: int, d: int) -> None:
result = 2 * c
t.log_outputs({"d": result}) # Log run outputs
assert result == d
这将创建/同步名称为“test_cd”的示例,输入{"c": 5}和参考输出{"d": 6},然后运行输出{"d": 10}.
日志反馈
默认情况下,LangSmith 在passfeedback 键。
您可以使用log_feedback.
import openai
import pytest
from langsmith import wrappers
from langsmith import testing as t
oai_client = wrappers.wrap_openai(openai.OpenAI())
@pytest.mark.langsmith
def test_offtopic_input() -> None:
user_query = "whats up"
t.log_inputs({"user_query": user_query})
sql = generate_sql(user_query)
t.log_outputs({"sql": sql})
expected = "Sorry that is not a valid query."
t.log_reference_outputs({"sql": expected})
# Use this context manager to trace any steps used for generating evaluation
# feedback separately from the main application logic
with t.trace_feedback():
instructions = (
"Return 1 if the ACTUAL and EXPECTED answers are semantically equivalent, "
"otherwise return 0. Return only 0 or 1 and nothing else."
)
grade = oai_client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o-mini",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": instructions},
{"role": "user", "content": f"ACTUAL: {sql}\nEXPECTED: {expected}"},
],
)
score = float(grade.choices[0].message.content)
t.log_feedback(key="correct", score=score)
assert score
请注意trace_feedback()上下文管理器。这使得 LLM-as-judge 调用与测试用例的其余部分分开跟踪。
它不会显示在主测试用例运行中,而是显示在correctfeedback 键。
注意: 请确保log_feedback与反馈跟踪关联的调用发生在trace_feedback上下文。
这样,我们就能将反馈与跟踪相关联,当在 UI 中看到反馈时,您可以单击它来查看生成反馈的跟踪。
跟踪中间调用
LangSmith 将自动跟踪测试用例执行过程中发生的任何可跟踪的中间调用。
将测试分组到测试套件中
默认情况下,给定文件中的所有测试都将分组为具有相应数据集的单个“测试套件”。
您可以通过传递test_suite_name参数设置为@pytest.mark.langsmith进行逐个案例分组,或者您可以设置LANGSMITH_TEST_SUITEenv var 将执行中的所有测试分组到单个测试套件中:
LANGSMITH_TEST_SUITE="SQL app tests" pytest tests/
我们通常建议设置LANGSMITH_TEST_SUITE以获取所有结果的整合视图。
命名实验
您可以使用LANGSMITH_EXPERIMENTenv var 中:
LANGSMITH_TEST_SUITE="SQL app tests" LANGSMITH_EXPERIMENT="baseline" pytest tests/
缓存
CI 中每个提交的 LLM 可能会变得昂贵。
为了节省时间和资源,LangSmith 允许您将 HTTP 请求缓存到磁盘。
要启用缓存,请使用langsmith[pytest]并设置 env varLANGSMITH_TEST_CACHE=/my/cache/path:
pip install -U "langsmith[pytest]"
LANGSMITH_TEST_CACHE=tests/cassettes pytest tests/my_llm_tests
所有请求都将被缓存到tests/cassettes并在后续运行中从那里加载。如果您将其签入存储库,您的 CI 也将能够使用缓存。
pytest 功能
@pytest.mark.langsmith旨在避免您的干扰,并与 Familiar 配合使用pytest特征。
参数化pytest.mark.parametrize
您可以使用parametrizedecorator 的 intent 和以前一样。
这将为测试的每个参数化实例创建一个新的测试用例。
@pytest.mark.langsmith(output_keys=["expected_sql"])
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
"user_query, expected_sql",
[
("Get all users from the customers table", "SELECT * FROM customers"),
("Get all users from the orders table", "SELECT * FROM orders"),
],
)
def test_sql_generation_parametrized(user_query, expected_sql):
sql = generate_sql(user_query)
assert sql == expected_sql
注意:随着参数化列表的增长,您可以考虑使用evaluate()相反。这将并行化评估,并更容易控制单个实验和相应的数据集。
并行化pytest-xdist
您可以像往常一样使用 pytest-xdist 来并行执行测试:
pip install -U pytest-xdist
pytest -n auto tests
异步测试pytest-asyncio
@pytest.mark.langsmith适用于 Sync 或 Async 测试,因此您可以完全像以前一样运行异步测试。
观看模式与pytest-watch
使用监视模式快速迭代您的测试。我们强烈建议在启用测试缓存(见下文)的情况下使用它,以避免不必要的 LLM 调用:
pip install pytest-watch
LANGSMITH_TEST_CACHE=tests/cassettes ptw tests/my_llm_tests
丰富的输出
如果您希望查看测试运行的 LangSmith 结果的丰富显示,您可以指定--langsmith-output:
pytest --langsmith-output tests
注意:这个标志曾经是--output=langsmith在langsmith<=0.3.3但已更新以避免与其他 Pytest 插件发生冲突。
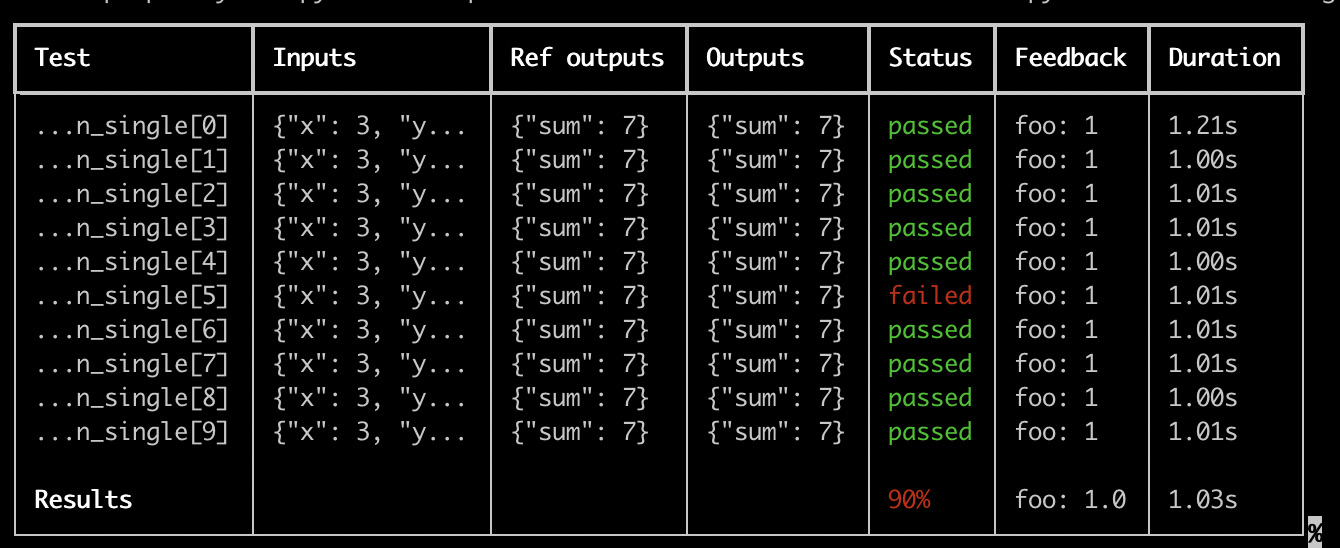
您将获得每个测试套件的精美表格,该表格会在结果上传到 LangSmith 时实时更新:
使用此功能的一些重要说明:
- 确保您已安装
pip install -U "langsmith[pytest]" - 丰富的输出当前无法使用
pytest-xdist
注意:自定义输出会删除所有标准的 pytest 输出。 如果你试图调试一些意外的行为,通常最好显示常规的 pytest 输出,以获得完整的错误跟踪。
空运行模式
如果要在不将结果同步到 LangSmith 的情况下运行测试,则可以设置LANGSMITH_TEST_TRACKING=false在您的环境中。
LANGSMITH_TEST_TRACKING=false pytest tests/
测试将正常运行,但实验日志不会发送到 LangSmith。
期望值
LangSmith 提供了一个 expect 实用程序来帮助定义对 LLM 输出的期望。例如:
from langsmith import expect
@pytest.mark.langsmith
def test_sql_generation_select_all():
user_query = "Get all users from the customers table"
sql = generate_sql(user_query)
expect(sql).to_contain("customers")
此外,这会将二进制 “expectation” 分数记录到实验结果中assert满足预期可能会触发测试失败。
expect还提供 “fuzzy match” 方法。例如:
@pytest.mark.langsmith(output_keys=["expectation"])
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
"query, expectation",
[
("what's the capital of France?", "Paris"),
],
)
def test_embedding_similarity(query, expectation):
prediction = my_chatbot(query)
expect.embedding_distance(
# This step logs the distance as feedback for this run
prediction=prediction, expectation=expectation
# Adding a matcher (in this case, 'to_be_*"), logs 'expectation' feedback
).to_be_less_than(0.5) # Optional predicate to assert against
expect.edit_distance(
# This computes the normalized Damerau-Levenshtein distance between the two strings
prediction=prediction, expectation=expectation
# If no predicate is provided below, 'assert' isn't called, but the score is still logged
)
此测试用例将被分配 4 个分数:
- 这
embedding_distance在预测与期望之间 - 二进制文件
expectation分数(如果余弦距离小于 0.5,则为 1,否则为 0) - 这
edit_distance在预测与期望之间 - 总体测试通过/失败分数(二进制)
这expectutility 以 Jest 的 expect API 为蓝本,具有一些现成的功能,可以更轻松地对 LLM 进行分级。
遗产
@test / @unit装饰
标记测试用例的传统方法是使用@test或@unit装饰:
from langsmith import test
@test
def test_foo() -> None:
pass