如何运行成对评估
LangSmith 支持以比较方式评估现有实验。 这使您可以对多个实验的输出进行相互评分,而不是局限于一次评估一个输出。 想想 LMSYS Chatbot Arena - 这是同一个概念! 为此,请将 evaluate() 函数与两个现有实验一起使用。
如果您尚未创建要比较的实验,请查看我们的快速入门或操作指南以开始使用评估。
evaluate()比较 args
本指南要求langsmithPython 版本>=0.2.0或 JS 版本>=0.2.9.
简单来说,evaluate / aevaluatefunction 接受以下参数:
| 论点 | 描述 |
|---|---|
target | A list of the two existing experiments you would like to evaluate against each other. These can be uuids or experiment names. |
evaluators | A list of the pairwise evaluators that you would like to attach to this evaluation. See the section below for how to define these. |
除此之外,您还可以传入以下可选 args:
| 论点 | 描述 |
|---|---|
randomize_order / randomizeOrder | An optional boolean indicating whether the order of the outputs should be randomized for each evaluation. This is a strategy for minimizing positional bias in your prompt: often, the LLM will be biased towards one of the responses based on the order. This should mainly be addressed via prompt engineering, but this is another optional mitigation. Defaults to False. |
experiment_prefix / experimentPrefix | A prefix to be attached to the beginning of the pairwise experiment name. Defaults to None. |
description | A description of the pairwise experiment. Defaults to None. |
max_concurrency / maxConcurrency | The maximum number of concurrent evaluations to run. Defaults to 5. |
client | The LangSmith client to use. Defaults to None. |
metadata | Metadata to attach to your pairwise experiment. Defaults to None. |
load_nested / loadNested | Whether to load all child runs for the experiment. When False, only the root trace will be passed to your evaluator. Defaults to False. |
定义成对赋值器
成对求值器只是具有预期签名的函数。
Evaluator args
自定义计算器函数必须具有特定的参数名称。它们可以采用以下参数的任何子集:
inputs: dict:与数据集中的单个示例对应的输入字典。outputs: list[dict]:每个实验对给定输入生成的 dict 输出的两项列表。reference_outputs/referenceOutputs: dict:与示例关联的参考输出的字典(如果可用)。runs: list[Run]:由给定示例的两个实验生成的完整 Run 对象的两项列表。如果您需要访问有关每次运行的中间步骤或元数据,请使用此选项。example: Example:完整数据集示例,包括示例输入、输出(如果可用)和 metdata(如果可用)。
对于大多数用例,您只需要inputs,outputs和reference_outputs / referenceOutputs.run和example仅当您需要应用程序的实际输入和输出之外的一些额外跟踪或示例元数据时,才有用。
赋值器输出
自定义计算器应返回以下类型之一:
Python 和 JS/TS
dict: 带键的字典:key,它表示将记录的反馈键scores,这是从运行 ID 到该运行分数的映射。comment,它是一个字符串。最常用于模型推理。
目前仅限 Python
list[int | float | bool]:一个包含两项的分数列表。假定该列表的顺序与runs/outputsevaluator args 的 Args 中。评估器函数名称用于反馈键。
请注意,您应该选择与运行时的标准反馈不同的反馈密钥。我们建议在成对反馈键前加上pairwise_或ranked_.
运行成对评估
以下示例使用一个提示,要求 LLM 决定两个 AI 助手响应之间哪个更好。它使用结构化输出来解析 AI 的响应:0、1 或 2。
在下面的 Python 示例中,我们从 LangChain Hub 中提取此结构化提示,并将其与 LangChain 聊天模型包装器一起使用。
使用 LangChain 是完全可选的。为了说明这一点,TypeScript 示例直接使用了 OpenAI SDK。
- 蟒
- TypeScript (类型脚本)
需要langsmith>=0.2.0
from langchain import hub
from langchain.chat_models import init_chat_model
from langsmith import evaluate
# See the prompt: https://smith.langchain.com/hub/langchain-ai/pairwise-evaluation-2
prompt = hub.pull("langchain-ai/pairwise-evaluation-2")
model = init_chat_model("gpt-4o")
chain = prompt | model
def ranked_preference(inputs: dict, outputs: list[dict]) -> list:
# Assumes example inputs have a 'question' key and experiment
# outputs have an 'answer' key.
response = chain.invoke({
"question": inputs["question"],
"answer_a": outputs[0].get("answer", "N/A"),
"answer_b": outputs[1].get("answer", "N/A"),
})
if response["Preference"] == 1:
scores = [1, 0]
elif response["Preference"] == 2:
scores = [0, 1]
else:
scores = [0, 0]
return scores
evaluate(
("experiment-1", "experiment-2"), # Replace with the names/IDs of your experiments
evaluators=[ranked_preference],
randomize_order=True,
max_concurrency=4,
)
Requires langsmith>=0.2.9
import { evaluate} from "langsmith/evaluation";
import { Run } from "langsmith/schemas";
import { wrapOpenAI } from "langsmith/wrappers";
import OpenAI from "openai";
import { z } from "zod";
const openai = wrapOpenAI(new OpenAI());
async function rankedPreference({
inputs,
runs,
}: {
inputs: Record<string, any>;
runs: Run[];
}) {
const scores: Record<string, number> = {};
const [runA, runB] = runs;
if (!runA || !runB) throw new Error("Expected at least two runs");
const payload = {
question: inputs.question,
answer_a: runA?.outputs?.output ?? "N/A",
answer_b: runB?.outputs?.output ?? "N/A",
};
const output = await openai.chat.completions.create({
model: "gpt-4-turbo",
messages: [
{
role: "system",
content: [
"Please act as an impartial judge and evaluate the quality of the responses provided by two AI assistants to the user question displayed below.",
"You should choose the assistant that follows the user's instructions and answers the user's question better.",
"Your evaluation should consider factors such as the helpfulness, relevance, accuracy, depth, creativity, and level of detail of their responses.",
"Begin your evaluation by comparing the two responses and provide a short explanation.",
"Avoid any position biases and ensure that the order in which the responses were presented does not influence your decision.",
"Do not allow the length of the responses to influence your evaluation. Do not favor certain names of the assistants. Be as objective as possible.",
].join(" "),
},
{
role: "user",
content: [
`[User Question] ${payload.question}`,
`[The Start of Assistant A's Answer] ${payload.answer_a} [The End of Assistant A's Answer]`,
`The Start of Assistant B's Answer] ${payload.answer_b} [The End of Assistant B's Answer]`,
].join("\n\n"),
},
],
tool_choice: {
type: "function",
function: { name: "Score" },
},
tools: [
{
type: "function",
function: {
name: "Score",
description: [
`After providing your explanation, output your final verdict by strictly following this format:`,
`Output "1" if Assistant A answer is better based upon the factors above.`,
`Output "2" if Assistant B answer is better based upon the factors above.`,
`Output "0" if it is a tie.`,
].join(" "),
parameters: {
type: "object",
properties: {
Preference: {
type: "integer",
description: "Which assistant answer is preferred?",
},
},
},
},
},
],
});
const { Preference } = z
.object({ Preference: z.number() })
.parse(
JSON.parse(output.choices[0].message.tool_calls[0].function.arguments)
);
if (Preference === 1) {
scores[runA.id] = 1;
scores[runB.id] = 0;
} else if (Preference === 2) {
scores[runA.id] = 0;
scores[runB.id] = 1;
} else {
scores[runA.id] = 0;
scores[runB.id] = 0;
}
return { key: "ranked_preference", scores };
}
await evaluate(["earnest-name-40", "reflecting-pump-91"], {
evaluators: [rankedPreference],
});
查看成对实验
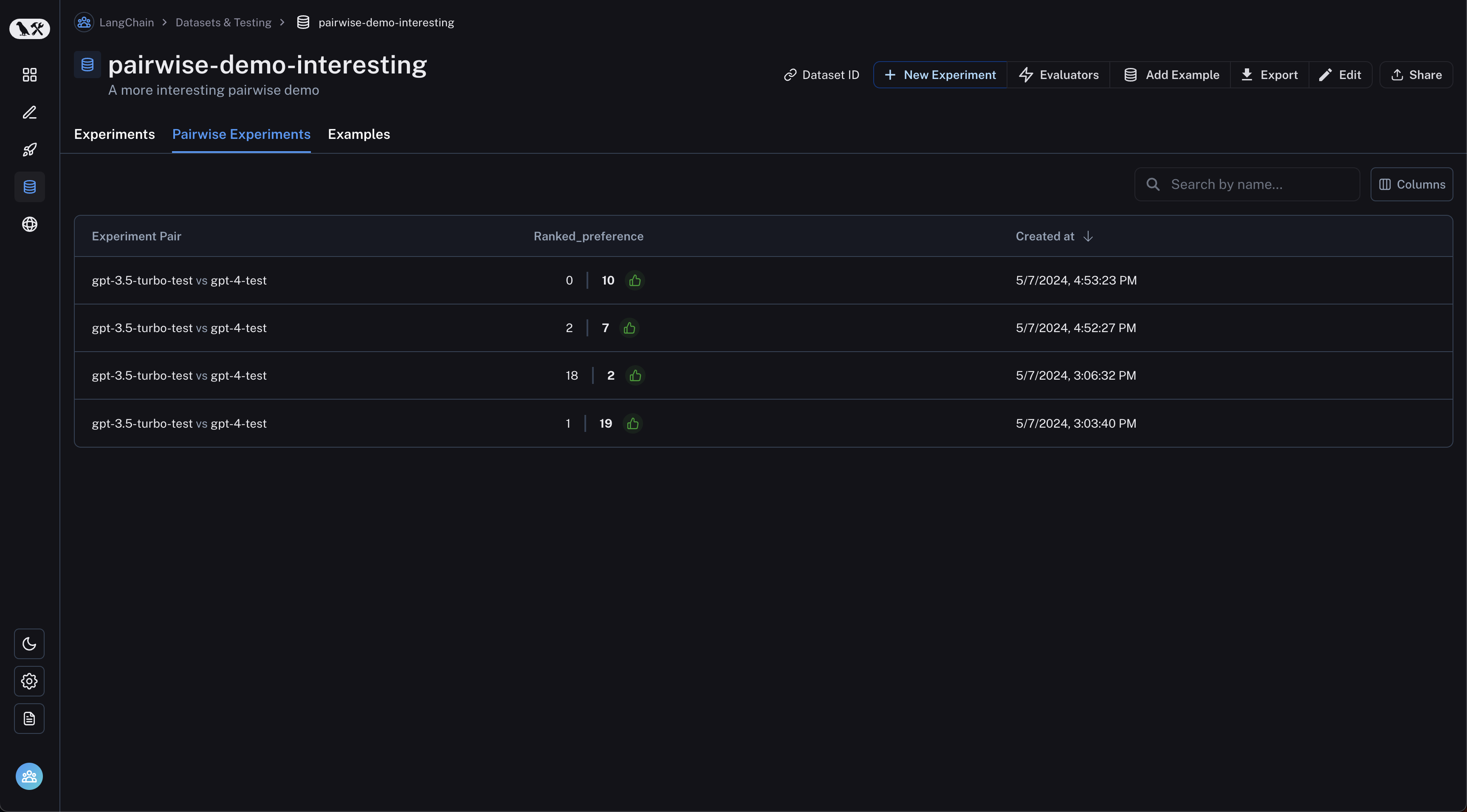
从数据集页面导航到 “Pairwise Experiments” 选项卡:
单击要检查的成对实验,您将进入 Comparison View:
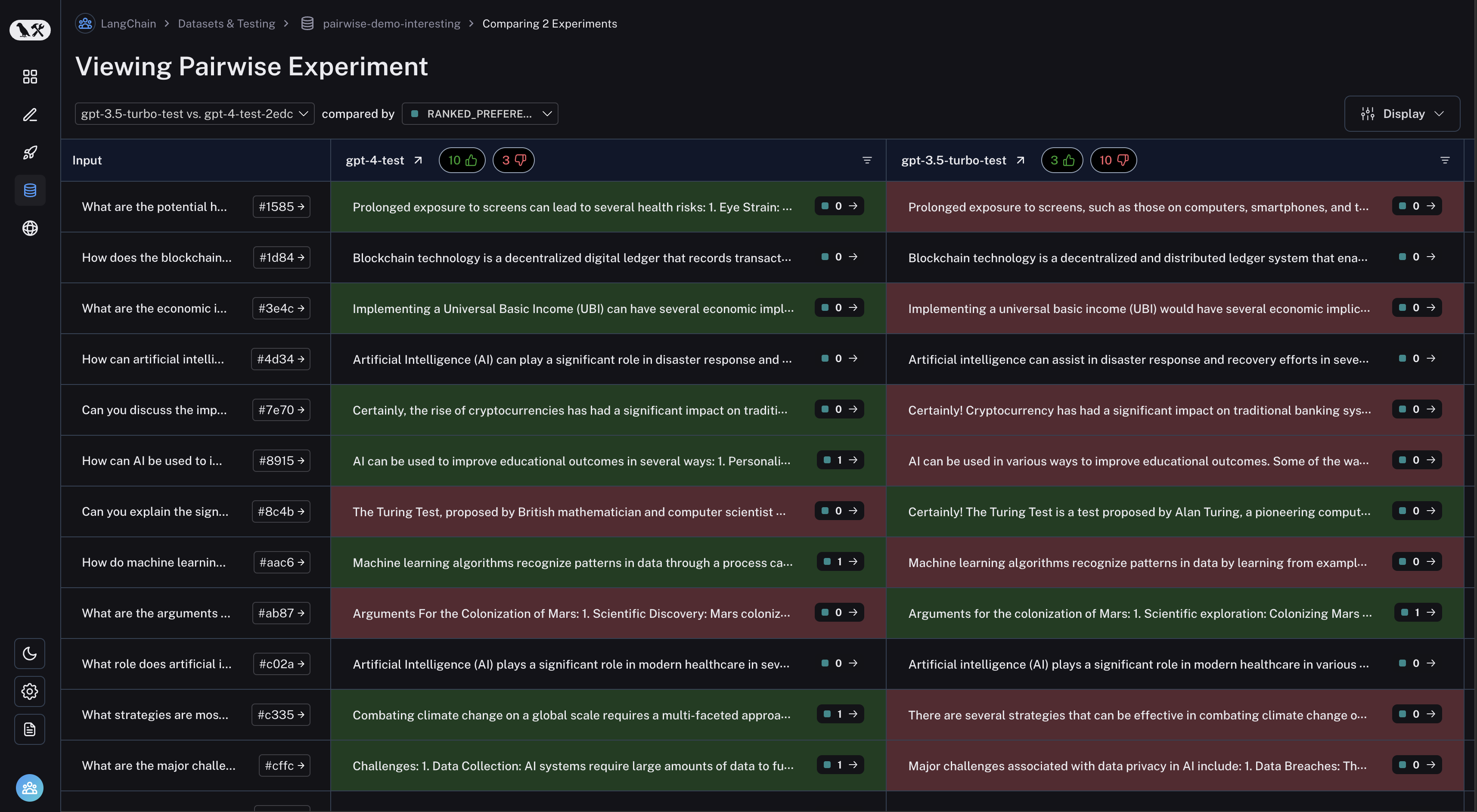
您可以通过单击表标题中的竖起大拇指/竖起大拇指按钮来筛选第一个实验效果更好的运行,反之亦然: