检索
这里回顾的一些概念利用模型来生成查询(例如,用于 SQL 或图形数据库)。 这样做存在固有的风险。 确保您的数据库连接权限的范围尽可能窄,以满足您的应用程序需求。 这将减轻(但不能消除)构建能够查询数据库的模型驱动系统的风险。 有关一般安全最佳实践的更多信息,请参阅我们的安全指南。
概述
检索系统是许多 AI 应用程序的基础,可以有效地从大型数据集中识别相关信息。 这些系统支持各种数据格式:
- 非结构化文本(例如,文档)通常存储在向量存储或词法搜索索引中。
- 结构化数据通常存储在具有定义架构的关系数据库或图形数据库中。
尽管数据格式越来越多样化,但现代 AI 应用程序越来越致力于通过自然语言界面访问所有类型的数据。 模型在此过程中发挥着至关重要的作用,它将自然语言查询转换为与基础搜索索引或数据库兼容的格式。 这种转换支持与复杂数据结构进行更直观、更灵活的交互。
关键概念
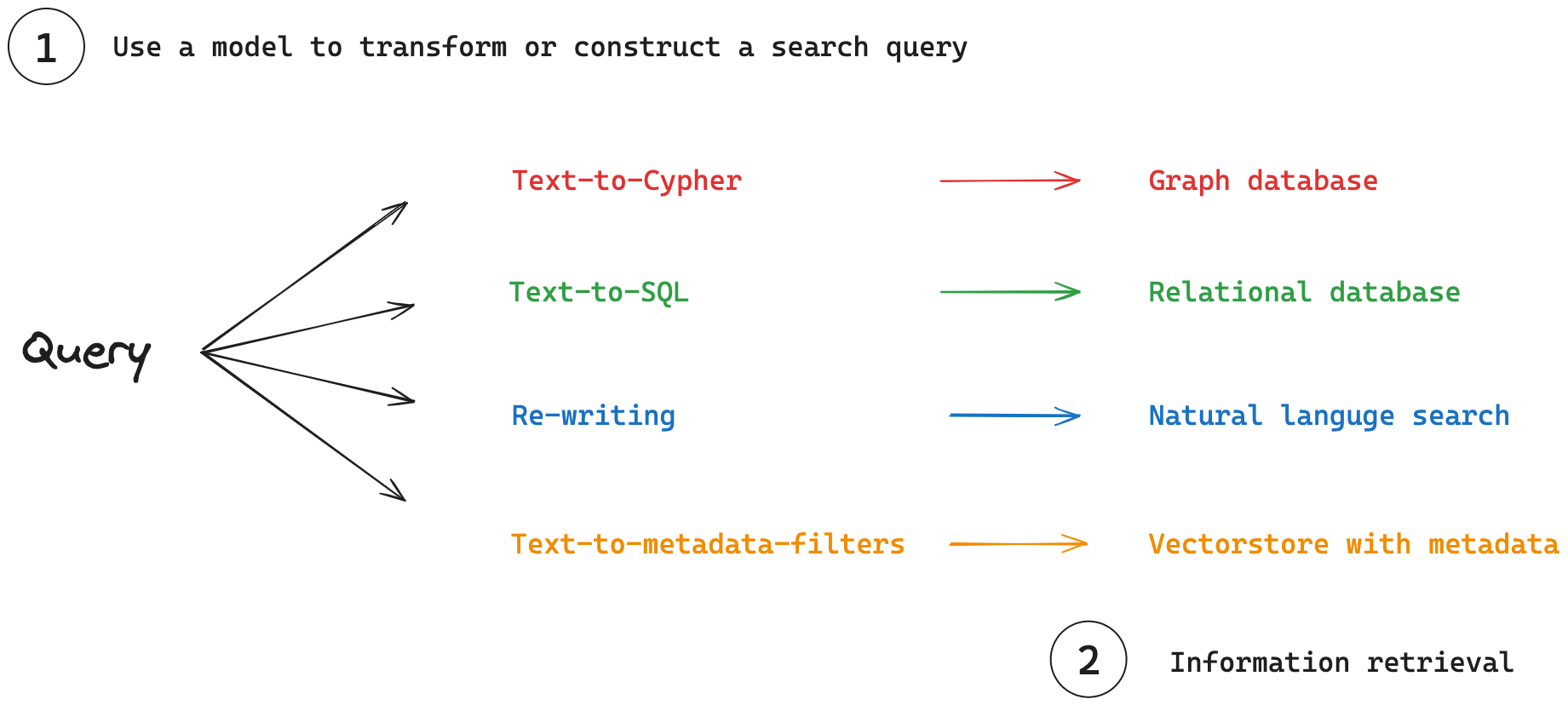
(1) 查询分析:模型转换或构建搜索查询以优化检索的过程。
(2) 信息检索:搜索查询用于从各种检索系统中获取信息。
查询分析
虽然用户通常更喜欢使用自然语言与检索系统交互,但这些系统可能需要特定的查询语法或受益于某些关键字。 查询分析充当原始用户输入和优化搜索查询之间的桥梁。查询分析的一些常见应用包括:
- 查询重写:可以重写或扩展查询,以改进语义或词法搜索。
- 查询构造:搜索索引可能需要结构化查询(例如,用于数据库的 SQL)。
查询分析使用模型根据原始用户输入转换或构建优化的搜索查询。
查询重写
理想情况下,检索系统应该处理广泛的用户输入,从简单和措辞不佳的查询到复杂的多方面问题。 为了实现这种多功能性,一种流行的方法是使用模型将原始用户查询转换为更有效的搜索查询。 这种转换的范围可以从简单的关键字提取到复杂的查询扩展和重新表述。 以下是在非结构化数据检索中使用模型进行查询分析的一些主要好处:
- 查询澄清:为了清晰起见,模型可以改写模棱两可或措辞不佳的查询。
- 语义理解:他们可以捕捉查询背后的意图,而不仅仅是文字上的关键字匹配。
- 查询扩展:模型可以生成相关术语或概念以扩大搜索范围。
- 复杂的查询处理:他们可以将多部分问题分解为更简单的子查询。
已经开发了各种技术来利用模型进行查询重写,包括:
| 名字 | 适用情形 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| Multi-query | When you want to ensure high recall in retrieval by providing multiple phrasings of a question. | Rewrite the user question with multiple phrasings, retrieve documents for each rewritten question, return the unique documents for all queries. |
| Decomposition | When a question can be broken down into smaller subproblems. | Decompose a question into a set of subproblems / questions, which can either be solved sequentially (use the answer from first + retrieval to answer the second) or in parallel (consolidate each answer into final answer). |
| Step-back | When a higher-level conceptual understanding is required. | First prompt the LLM to ask a generic step-back question about higher-level concepts or principles, and retrieve relevant facts about them. Use this grounding to help answer the user question. Paper. |
| HyDE | If you have challenges retrieving relevant documents using the raw user inputs. | Use an LLM to convert questions into hypothetical documents that answer the question. Use the embedded hypothetical documents to retrieve real documents with the premise that doc-doc similarity search can produce more relevant matches. Paper. |
例如,查询分解可以简单地使用提示和强制执行子问题列表的结构化输出来完成。 然后,这些可以在下游检索系统上按顺序或并行运行。
from typing import List
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain_core.messages import SystemMessage, HumanMessage
# Define a pydantic model to enforce the output structure
class Questions(BaseModel):
questions: List[str] = Field(
description="A list of sub-questions related to the input query."
)
# Create an instance of the model and enforce the output structure
model = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o", temperature=0)
structured_model = model.with_structured_output(Questions)
# Define the system prompt
system = """You are a helpful assistant that generates multiple sub-questions related to an input question. \n
The goal is to break down the input into a set of sub-problems / sub-questions that can be answered independently. \n"""
# Pass the question to the model
question = """What are the main components of an LLM-powered autonomous agent system?"""
questions = structured_model.invoke([SystemMessage(content=system)]+[HumanMessage(content=question)])
查询构造
查询分析还可以专注于将自然语言查询转换为专门的查询语言或筛选器。 这种转换对于与包含结构化或半结构化数据的各种类型的数据库有效交互至关重要。
-
结构化数据示例:对于关系数据库和图形数据库,使用域特定语言 (DSL) 来查询数据。
- Text-to-SQL:将关系数据库的自然语言转换为 SQL。
- Text-to-Cypher:将自然语言转换为图形数据库的 Cypher。
-
半结构化数据示例:对于 vectorstore,查询可以将语义搜索与元数据筛选相结合。
- Natural Language to Metadata Filters(自然语言到元数据过滤器):将用户查询转换为适当的元数据过滤器。
这些方法利用模型来弥合用户意图与不同数据存储系统的特定查询要求之间的差距。以下是一些流行的技术:
| 名字 | 适用情形 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| Self Query | If users are asking questions that are better answered by fetching documents based on metadata rather than similarity with the text. | This uses an LLM to transform user input into two things: (1) a string to look up semantically, (2) a metadata filter to go along with it. This is useful because oftentimes questions are about the METADATA of documents (not the content itself). |
| Text to SQL | If users are asking questions that require information housed in a relational database, accessible via SQL. | This uses an LLM to transform user input into a SQL query. |
| Text-to-Cypher | If users are asking questions that require information housed in a graph database, accessible via Cypher. | This uses an LLM to transform user input into a Cypher query. |
例如,以下是如何使用SelfQueryRetriever将自然语言查询转换为元数据筛选器。
metadata_field_info = schema_for_metadata
document_content_description = "Brief summary of a movie"
llm = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0)
retriever = SelfQueryRetriever.from_llm(
llm,
vectorstore,
document_content_description,
metadata_field_info,
)
- 请参阅我们关于文本到 SQL、文本到密码和元数据过滤器查询分析的教程。
- 请参阅我们的博客文章概述。
- 请参阅我们关于查询构建的 RAG from Scratch 视频。
信息检索
常见检索系统
词法搜索索引
许多搜索引擎都基于查询中的单词与每个文档中的单词的匹配。 这种方法称为词法检索,使用通常基于词频的搜索算法。 直觉很简单:一个词在用户的查询和特定文档中都频繁出现,那么这个文档可能是一个很好的匹配项。
用于实现此目的的特定数据结构通常是倒排索引。 这种类型的索引包含一个单词列表和每个单词到它在各种文档中出现的位置列表的映射。 使用此数据结构,可以有效地将搜索查询中的单词与它们所在的文档进行匹配。BM25 和 TF-IDF 是两种流行的词法搜索算法。
- 请参阅 BM25 retriever 集成。
- 请参阅 Elasticsearch 检索器集成。
向量索引
矢量索引是索引和存储非结构化数据的另一种方法。
有关详细概述,请参阅我们关于 vectorstores 的概念指南。
简而言之,向量存储不使用词频,而是使用嵌入模型将文档压缩为高维向量表示。
这允许使用简单的数学运算(如余弦相似度)对嵌入向量进行高效的相似性搜索。
- 有关使用 vectorstore 的更多详细信息,请参阅我们的操作指南。
- 请参阅我们的 vectorstore 集成列表。
- 请参阅 Cameron Wolfe 的博客文章,了解向量搜索的基础知识。
关系数据库
关系数据库是许多应用程序中使用的一种基本类型的结构化数据存储。 它们将数据组织到具有预定义架构的表中,其中每个表代表一个实体或关系。 数据存储在行 (记录) 和列 (属性) 中,允许通过 SQL(结构化查询语言)进行高效的查询和作。 关系数据库擅长维护数据完整性、支持复杂查询以及处理不同数据实体之间的关系。
- 请参阅我们的教程,了解如何使用 SQL 数据库。
- 请参阅我们的 SQL 数据库工具包。
图形数据库
图形数据库是一种特殊类型的数据库,旨在存储和管理高度互连的数据。 与传统的关系数据库不同,图形数据库使用由节点(实体)、边缘(关系)和属性组成的灵活结构。 此结构允许有效地表示和查询复杂的互连数据。 图形数据库以图形结构存储数据,具有节点、边缘和属性。 它们对于存储和查询数据点之间的复杂关系特别有用,例如社交网络、供应链管理、欺诈检测和推荐服务
- 请参阅我们的教程,了解如何使用图形数据库。
- 请参阅我们的图形数据库集成列表。
- 请参阅 Neo4j 的 LangChain 初学者工具包。
Retriever
LangChain 提供了一个统一的接口,用于通过 retriever 概念与各种检索系统进行交互。界面很简单:
- 输入:查询 (string)
- 输出:文档列表(标准化的 LangChain Document 对象)
您可以使用前面提到的任何检索系统创建检索器。我们讨论的查询分析技术在这里特别有用,因为它们为通常需要结构化查询语言的数据库启用了自然语言接口。
例如,您可以使用文本到 SQL 转换为 SQL 数据库构建检索器。这允许在后台将自然语言查询 (string) 转换为 SQL 查询。
无论底层检索系统如何,LangChain 中的所有检索器都共享一个通用接口。您可以将它们与简单的invoke方法:
docs = retriever.invoke(query)
- 请参阅我们关于Retriever的概念指南。
- 请参阅我们关于使用Retriever的操作指南。
