跟踪LangGraph(Python 和 JS/TS)
LangSmith 与 LangGraph(Python 和 JS)无缝集成 帮助您跟踪代理工作流,无论您使用的是 LangChain 模块还是其他 SDK。
使用 LangChain
如果你在 LangGraph 中使用 LangChain 模块,你只需要设置几个环境变量来启用跟踪。
本指南将介绍一个基本示例。有关配置的更多详细信息,请参阅使用 LangChain 进行跟踪指南。
1. 安装
安装 LangGraph 库以及适用于 Python 和 JS 的 OpenAI 集成(我们对下面的代码片段使用 OpenAI 集成)。
有关可用软件包的完整列表,请参阅 LangChain Python 文档和 LangChain JS 文档。
- 果仁
- 纱
- npm
- PNPM
pip install langchain_openai langgraph
yarn add @langchain/openai @langchain/langgraph
npm install @langchain/openai @langchain/langgraph
pnpm add @langchain/openai @langchain/langgraph
2. 配置您的环境
- 蟒
- TypeScript (类型脚本)
export LANGSMITH_TRACING=true
export LANGSMITH_API_KEY=<your-api-key>
# This example uses OpenAI, but you can use any LLM provider of choice
export OPENAI_API_KEY=<your-openai-api-key>
export LANGSMITH_TRACING=true
export LANGSMITH_API_KEY=<your-api-key>
# This example uses OpenAI, but you can use any LLM provider of choice
export OPENAI_API_KEY=<your-openai-api-key>
If you are using LangChain.js with LangSmith and are not in a serverless environment, we also recommend setting the following explicitly to reduce latency:
export LANGCHAIN_CALLBACKS_BACKGROUND=true
If you are in a serverless environment, we recommend setting the reverse to allow tracing to finish before your function ends:
export LANGCHAIN_CALLBACKS_BACKGROUND=false
See this LangChain.js guide for more information.
3. 记录跟踪记录
设置环境后,您可以照常调用 LangChain runnables。 LangSmith 将推断出正确的跟踪配置:
- 蟒
- TypeScript (类型脚本)
from typing import Literal
from langchain_core.messages import HumanMessage
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain_core.tools import tool
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, MessagesState
from langgraph.prebuilt import ToolNode
@tool
def search(query: str):
"""Call to surf the web."""
if "sf" in query.lower() or "san francisco" in query.lower():
return "It's 60 degrees and foggy."
return "It's 90 degrees and sunny."
tools = [search]
tool_node = ToolNode(tools)
model = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o", temperature=0).bind_tools(tools)
def should_continue(state: MessagesState) -> Literal["tools", "__end__"]:
messages = state['messages']
last_message = messages[-1]
if last_message.tool_calls:
return "tools"
return "__end__"
def call_model(state: MessagesState):
messages = state['messages']
# Invoking `model` will automatically infer the correct tracing context
response = model.invoke(messages)
return {"messages": [response]}
workflow = StateGraph(MessagesState)
workflow.add_node("agent", call_model)
workflow.add_node("tools", tool_node)
workflow.add_edge("__start__", "agent")
workflow.add_conditional_edges(
"agent",
should_continue,
)
workflow.add_edge("tools", 'agent')
app = workflow.compile()
final_state = app.invoke(
{"messages": [HumanMessage(content="what is the weather in sf")]},
config={"configurable": {"thread_id": 42}}
)
final_state["messages"][-1].content
import { HumanMessage, AIMessage } from "@langchain/core/messages";
import { tool } from "@langchain/core/tools";
import { z } from "zod";
import { ChatOpenAI } from "@langchain/openai";
import { StateGraph, StateGraphArgs } from "@langchain/langgraph";
import { ToolNode } from "@langchain/langgraph/prebuilt";
interface AgentState {
messages: HumanMessage[];
}
const graphState: StateGraphArgs<AgentState>["channels"] = {
messages: {
reducer: (x: HumanMessage[], y: HumanMessage[]) => x.concat(y),
},
};
const searchTool = tool(async ({ query }: { query: string }) => {
if (query.toLowerCase().includes("sf") || query.toLowerCase().includes("san francisco")) {
return "It's 60 degrees and foggy."
}
return "It's 90 degrees and sunny."
}, {
name: "search",
description:
"Call to surf the web.",
schema: z.object({
query: z.string().describe("The query to use in your search."),
}),
});
const tools = [searchTool];
const toolNode = new ToolNode<AgentState>(tools);
const model = new ChatOpenAI({
model: "gpt-4o",
temperature: 0,
}).bindTools(tools);
function shouldContinue(state: AgentState) {
const messages = state.messages;
const lastMessage = messages[messages.length - 1] as AIMessage;
if (lastMessage.tool_calls?.length) {
return "tools";
}
return "__end__";
}
async function callModel(state: AgentState) {
const messages = state.messages;
// Invoking `model` will automatically infer the correct tracing context
const response = await model.invoke(messages);
return { messages: [response] };
}
const workflow = new StateGraph<AgentState>({ channels: graphState })
.addNode("agent", callModel)
.addNode("tools", toolNode)
.addEdge("__start__", "agent")
.addConditionalEdges("agent", shouldContinue)
.addEdge("tools", "agent");
const app = workflow.compile();
const finalState = await app.invoke(
{ messages: [new HumanMessage("what is the weather in sf")] },
{ configurable: { thread_id: "42" } }
);
finalState.messages[finalState.messages.length - 1].content;
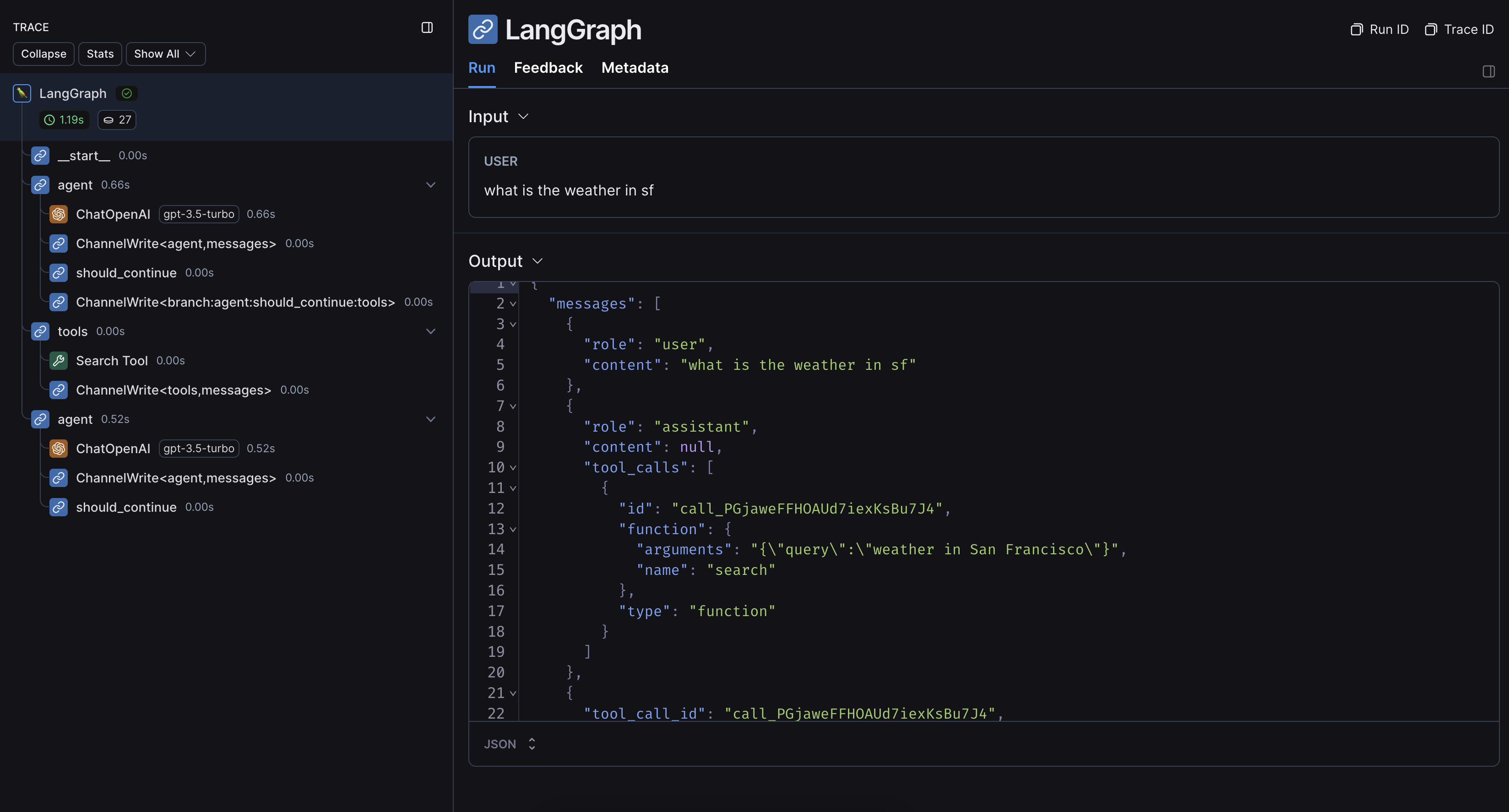
运行上述代码的示例跟踪如下所示:
不使用 LangChain
如果你在 LangGraph 中使用其他 SDK 或自定义函数,则需要适当地包装或装饰它们(使用@traceabledecorator 或traceable函数,或类似 JS 中的内容。wrap_openai用于 SDK)。
如果你这样做,LangSmith 将自动嵌套来自这些包装方法的跟踪。
下面是一个示例。您还可以查看此页面以了解更多信息。
1. 安装
安装 LangGraph 库和适用于 Python 和 JS 的 OpenAI SDK(我们对下面的代码片段使用 OpenAI 集成)。
- 果仁
- 纱
- npm
- PNPM
pip install openai langsmith langgraph
yarn add openai langsmith @langchain/langgraph
npm install openai langsmith @langchain/langgraph
pnpm add openai langsmith @langchain/langgraph
2. 配置您的环境
- 蟒
- TypeScript (类型脚本)
export LANGSMITH_TRACING=true
export LANGSMITH_API_KEY=<your-api-key>
# This example uses OpenAI, but you can use any LLM provider of choice
export OPENAI_API_KEY=<your-openai-api-key>
export LANGSMITH_TRACING=true
export LANGSMITH_API_KEY=<your-api-key>
# This example uses OpenAI, but you can use any LLM provider of choice
export OPENAI_API_KEY=<your-openai-api-key>
If you are using LangChain.js with LangSmith and are not in a serverless environment, we also recommend setting the following explicitly to reduce latency:
export LANGCHAIN_CALLBACKS_BACKGROUND=true
If you are in a serverless environment, we recommend setting the reverse to allow tracing to finish before your function ends:
export LANGCHAIN_CALLBACKS_BACKGROUND=false
See this LangChain.js guide for more information.
3. 记录跟踪记录
设置环境后,包装或装饰要跟踪的自定义函数/SDK。 然后,LangSmith 将推断正确的跟踪配置:
- 蟒
- TypeScript (类型脚本)
import json
import openai
import operator
from langsmith import traceable
from langsmith.wrappers import wrap_openai
from typing import Annotated, Literal, TypedDict
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph
class State(TypedDict):
messages: Annotated[list, operator.add]
tool_schema = {
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": "search",
"description": "Call to surf the web.",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {"query": {"type": "string"}},
"required": ["query"],
},
},
}
# Decorating the tool function will automatically trace it with the correct context
@traceable(run_type="tool", name="Search Tool")
def search(query: str):
"""Call to surf the web."""
if "sf" in query.lower() or "san francisco" in query.lower():
return "It's 60 degrees and foggy."
return "It's 90 degrees and sunny."
tools = [search]
def call_tools(state):
function_name_to_function = {"search": search}
messages = state["messages"]
tool_call = messages[-1]["tool_calls"][0]
function_name = tool_call["function"]["name"]
function_arguments = tool_call["function"]["arguments"]
arguments = json.loads(function_arguments)
function_response = function_name_to_function[function_name](**arguments)
tool_message = {
"tool_call_id": tool_call["id"],
"role": "tool",
"name": function_name,
"content": function_response,
}
return {"messages": [tool_message]}
wrapped_client = wrap_openai(openai.Client())
def should_continue(state: State) -> Literal["tools", "__end__"]:
messages = state["messages"]
last_message = messages[-1]
if last_message["tool_calls"]:
return "tools"
return "__end__"
def call_model(state: State):
messages = state["messages"]
# Calling the wrapped client will automatically infer the correct tracing context
response = wrapped_client.chat.completions.create(
messages=messages, model="gpt-4o-mini", tools=[tool_schema]
)
raw_tool_calls = response.choices[0].message.tool_calls
tool_calls = [tool_call.to_dict() for tool_call in raw_tool_calls] if raw_tool_calls else []
response_message = {
"role": "assistant",
"content": response.choices[0].message.content,
"tool_calls": tool_calls,
}
return {"messages": [response_message]}
workflow = StateGraph(State)
workflow.add_node("agent", call_model)
workflow.add_node("tools", call_tools)
workflow.add_edge("__start__", "agent")
workflow.add_conditional_edges(
"agent",
should_continue,
)
workflow.add_edge("tools", 'agent')
app = workflow.compile()
final_state = app.invoke(
{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "what is the weather in sf"}]}
)
final_state["messages"][-1]["content"]
Note: The below example requires langsmith>=0.1.39 and @langchain/langgraph>=0.0.31
import OpenAI from "openai";
import { StateGraph } from "@langchain/langgraph";
import { wrapOpenAI } from "langsmith/wrappers/openai";
import { traceable } from "langsmith/traceable";
type GraphState = {
messages: OpenAI.ChatCompletionMessageParam[];
};
const wrappedClient = wrapOpenAI(new OpenAI({}));
const toolSchema: OpenAI.ChatCompletionTool = {
type: "function",
function: {
name: "search",
description: "Use this tool to query the web.",
parameters: {
type: "object",
properties: {
query: {
type: "string",
},
},
required: ["query"],
}
}
};
// Wrapping the tool function will automatically trace it with the correct context
const search = traceable(async ({ query }: { query: string }) => {
if (
query.toLowerCase().includes("sf") ||
query.toLowerCase().includes("san francisco")
) {
return "It's 60 degrees and foggy.";
}
return "It's 90 degrees and sunny."
}, { run_type: "tool", name: "Search Tool" });
const callTools = async ({ messages }: GraphState) => {
const mostRecentMessage = messages[messages.length - 1];
const toolCalls = (mostRecentMessage as OpenAI.ChatCompletionAssistantMessageParam).tool_calls;
if (toolCalls === undefined || toolCalls.length === 0) {
throw new Error("No tool calls passed to node.");
}
const toolNameMap = {
search,
};
const functionName = toolCalls[0].function.name;
const functionArguments = JSON.parse(toolCalls[0].function.arguments);
const response = await toolNameMap[functionName](functionArguments);
const toolMessage = {
tool_call_id: toolCalls[0].id,
role: "tool",
name: functionName,
content: response,
}
return { messages: [toolMessage] };
}
const callModel = async ({ messages }: GraphState) => {
// Calling the wrapped client will automatically infer the correct tracing context
const response = await wrappedClient.chat.completions.create({
messages,
model: "gpt-4o-mini",
tools: [toolSchema],
});
const responseMessage = {
role: "assistant",
content: response.choices[0].message.content,
tool_calls: response.choices[0].message.tool_calls ?? [],
};
return { messages: [responseMessage] };
}
const shouldContinue = ({ messages }: GraphState) => {
const lastMessage =
messages[messages.length - 1] as OpenAI.ChatCompletionAssistantMessageParam;
if (
lastMessage?.tool_calls !== undefined &&
lastMessage?.tool_calls.length > 0
) {
return "tools";
}
return "__end__";
}
const workflow = new StateGraph<GraphState>({
channels: {
messages: {
reducer: (a: any, b: any) => a.concat(b),
}
}
});
const graph = workflow
.addNode("model", callModel)
.addNode("tools", callTools)
.addEdge("__start__", "model")
.addConditionalEdges("model", shouldContinue, {
tools: "tools",
__end__: "__end__",
})
.addEdge("tools", "model")
.compile();
await graph.invoke({
messages: [{ role: "user", content: "what is the weather in sf" }]
});
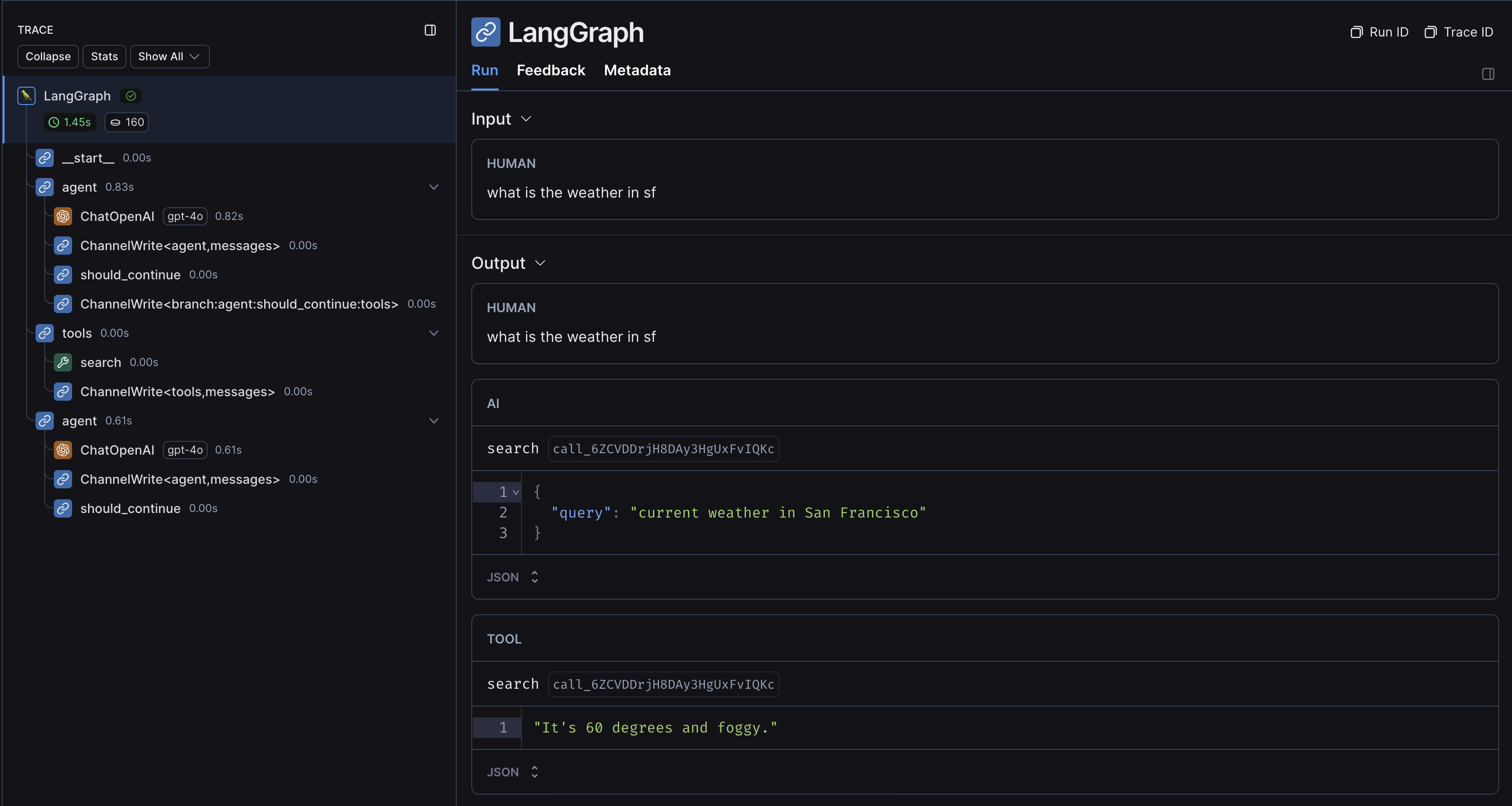
运行上述代码的示例跟踪如下所示: