跟踪LangChain(Python 和 JS/TS)
LangSmith 与 LangChain(Python 和 JS)无缝集成,后者是用于构建 LLM 应用程序的常用开源框架。
安装
安装核心库以及适用于 Python 和 JS 的 OpenAI 集成(我们对下面的代码片段使用 OpenAI 集成)。
有关可用软件包的完整列表,请参阅 LangChain Python 文档和 LangChain JS 文档。
- 果仁
- 纱
- npm
- PNPM
pip install langchain_openai langchain_core
yarn add @langchain/openai @langchain/core
npm install @langchain/openai @langchain/core
pnpm add @langchain/openai @langchain/core
快速开始
1. 配置您的环境
- 蟒
- TypeScript (类型脚本)
export LANGSMITH_TRACING=true
export LANGSMITH_API_KEY=<your-api-key>
# This example uses OpenAI, but you can use any LLM provider of choice
export OPENAI_API_KEY=<your-openai-api-key>
export LANGSMITH_TRACING=true
export LANGSMITH_API_KEY=<your-api-key>
# This example uses OpenAI, but you can use any LLM provider of choice
export OPENAI_API_KEY=<your-openai-api-key>
If you are using LangChain.js with LangSmith and are not in a serverless environment, we also recommend setting the following explicitly to reduce latency:
export LANGCHAIN_CALLBACKS_BACKGROUND=true
If you are in a serverless environment, we recommend setting the reverse to allow tracing to finish before your function ends:
export LANGCHAIN_CALLBACKS_BACKGROUND=false
See this LangChain.js guide for more information.
2. 记录跟踪
无需额外的代码即可将跟踪记录到 LangSmith。只需像往常一样运行你的 LangChain 代码。
- 蟒
- TypeScript (类型脚本)
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", "You are a helpful assistant. Please respond to the user's request only based on the given context."),
("user", "Question: {question}\nContext: {context}")
])
model = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o-mini")
output_parser = StrOutputParser()
chain = prompt | model | output_parser
question = "Can you summarize this morning's meetings?"
context = "During this morning's meeting, we solved all world conflict."
chain.invoke({"question": question, "context": context})
import { ChatOpenAI } from "@langchain/openai";
import { ChatPromptTemplate } from "@langchain/core/prompts";
import { StringOutputParser } from "@langchain/core/output_parsers";
const prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.fromMessages([
["system", "You are a helpful assistant. Please respond to the user's request only based on the given context."],
["user", "Question: {question}\nContext: {context}"],
]);
const model = new ChatOpenAI({ modelName: "gpt-4o-mini" });
const outputParser = new StringOutputParser();
const chain = prompt.pipe(model).pipe(outputParser);
const question = "Can you summarize this morning's meetings?"
const context = "During this morning's meeting, we solved all world conflict."
await chain.invoke({ question: question, context: context });
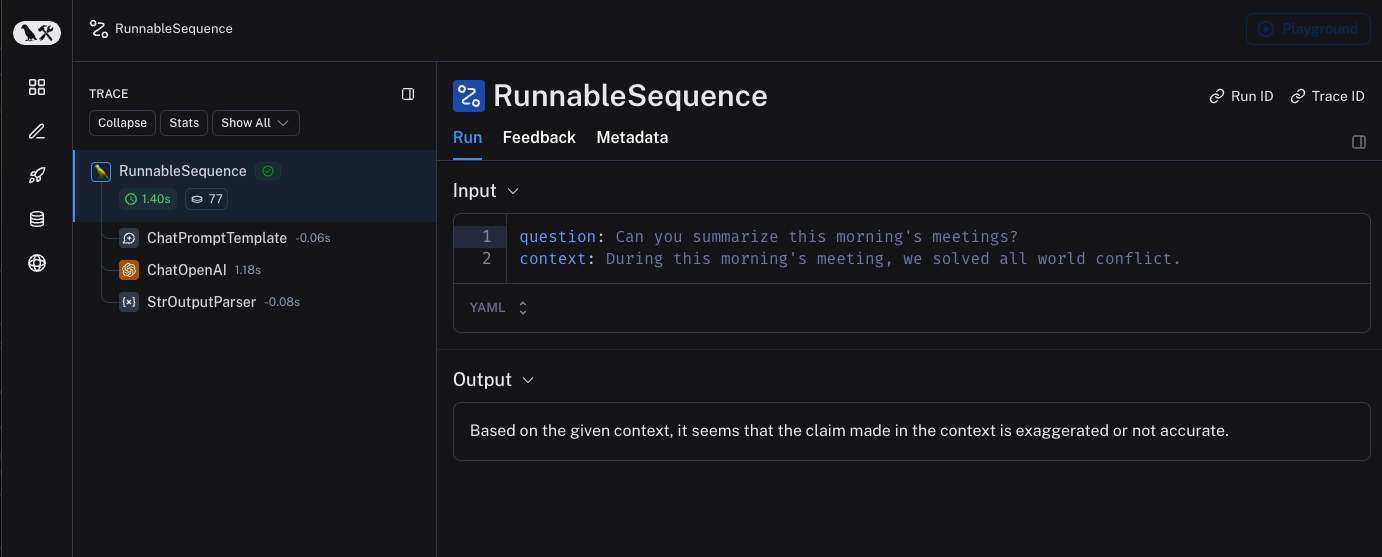
3. 查看跟踪记录
默认情况下,跟踪记录将记录到名称为default.使用上述代码记录的跟踪示例已公开,可在此处查看。
选择性跟踪
上一节展示了如何通过设置单个环境变量来跟踪应用程序中 LangChain Runnables 的所有调用。虽然这是一种方便的入门方法,但您可能希望仅跟踪应用程序的特定调用或部分。
在 Python 中有两种方法可以做到这一点:手动传入LangChainTracer (参考文档)实例作为回调,或者使用tracing_v2_enabled上下文管理器(参考文档)。
在 JS/TS 中,您可以传递一个LangChainTracer (参考文档)实例作为回调。
- 蟒
- TypeScript (类型脚本)
# You can configure a LangChainTracer instance to trace a specific invocation.
from langchain.callbacks.tracers import LangChainTracer
tracer = LangChainTracer()
chain.invoke({"question": "Am I using a callback?", "context": "I'm using a callback"}, config={"callbacks": [tracer]})
# LangChain Python also supports a context manager for tracing a specific block of code.
from langchain_core.tracers.context import tracing_v2_enabled
with tracing_v2_enabled():
chain.invoke({"question": "Am I using a context manager?", "context": "I'm using a context manager"})
# This will NOT be traced (assuming LANGSMITH_TRACING is not set)
chain.invoke({"question": "Am I being traced?", "context": "I'm not being traced"})
// You can configure a LangChainTracer instance to trace a specific invocation.
import { LangChainTracer } from "@langchain/core/tracers/tracer_langchain";
const tracer = new LangChainTracer();
await chain.invoke(
{
question: "Am I using a callback?",
context: "I'm using a callback"
},
{ callbacks: [tracer] }
);
记录到特定项目
静态
如跟踪概念指南中所述,LangSmith 使用 Project 的概念对跟踪进行分组。如果未指定,则跟踪器项目将设置为 default。您可以设置LANGSMITH_PROJECT环境变量为整个应用程序运行配置自定义项目名称。这应该在执行您的应用程序之前完成。
export LANGSMITH_PROJECT=my-project
这LANGSMITH_PROJECT标志仅在 JS SDK 版本 >= 0.2.16 中受支持,请使用LANGCHAIN_PROJECT相反,如果您使用的是旧版本。
动态
这在很大程度上构建在上一节的基础上,并允许您为特定的LangChainTracer实例或作为参数传递给tracing_v2_enabledPython 中的 context manager 来获取。
- 蟒
- TypeScript (类型脚本)
# You can set the project name for a specific tracer instance:
from langchain.callbacks.tracers import LangChainTracer
tracer = LangChainTracer(project_name="My Project")
chain.invoke({"question": "Am I using a callback?", "context": "I'm using a callback"}, config={"callbacks": [tracer]})
# You can set the project name using the project_name parameter.
from langchain_core.tracers.context import tracing_v2_enabled
with tracing_v2_enabled(project_name="My Project"):
chain.invoke({"question": "Am I using a context manager?", "context": "I'm using a context manager"})
// You can set the project name for a specific tracer instance:
import { LangChainTracer } from "@langchain/core/tracers/tracer_langchain";
const tracer = new LangChainTracer({ projectName: "My Project" });
await chain.invoke(
{
question: "Am I using a callback?",
context: "I'm using a callback"
},
{ callbacks: [tracer] }
);
向跟踪添加元数据和标签
您可以通过在 Config 中提供跟踪来发送带有任意元数据和标签的注释。 这对于将其他信息与跟踪相关联非常有用,例如执行跟踪的环境或启动跟踪的用户。 有关如何按元数据和标签查询跟踪和运行的信息,请参阅本指南
当您将元数据或标签附加到 Runnable 时(通过 RunnableConfig 或在运行时使用调用参数),它们将被该 Runnable 的所有子 Runnable 继承。
- 蟒
- TypeScript (类型脚本)
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", "You are a helpful AI."),
("user", "{input}")
])
# The tag "model-tag" and metadata {"model-key": "model-value"} will be attached to the ChatOpenAI run only
chat_model = ChatOpenAI().with_config({"tags": ["model-tag"], "metadata": {"model-key": "model-value"}})
output_parser = StrOutputParser()
# Tags and metadata can be configured with RunnableConfig
chain = (prompt | chat_model | output_parser).with_config({"tags": ["config-tag"], "metadata": {"config-key": "config-value"}})
# Tags and metadata can also be passed at runtime
chain.invoke({"input": "What is the meaning of life?"}, {"tags": ["invoke-tag"], "metadata": {"invoke-key": "invoke-value"}})
import { ChatOpenAI } from "@langchain/openai";
import { ChatPromptTemplate } from "@langchain/core/prompts";
import { StringOutputParser } from "@langchain/core/output_parsers";
const prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.fromMessages([
["system", "You are a helpful AI."],
["user", "{input}"]
])
// The tag "model-tag" and metadata {"model-key": "model-value"} will be attached to the ChatOpenAI run only
const model = new ChatOpenAI().withConfig({ tags: ["model-tag"], metadata: { "model-key": "model-value" } });
const outputParser = new StringOutputParser();
// Tags and metadata can be configured with RunnableConfig
const chain = (prompt.pipe(model).pipe(outputParser)).withConfig({"tags": ["config-tag"], "metadata": {"config-key": "top-level-value"}});
// Tags and metadata can also be passed at runtime
await chain.invoke({input: "What is the meaning of life?"}, {tags: ["invoke-tag"], metadata: {"invoke-key": "invoke-value"}})
自定义运行名称
在调用或流式传输 LangChain 代码时,您可以通过在 Config 中提供给定运行的名称来自定义该名称。
此名称用于标识 LangSmith 中的运行,并可用于筛选和分组运行。该名称还用作 LangSmith UI 中的运行标题。
这可以通过设置run_name在RunnableConfig对象,或者通过传递run_name在 JS/TS 的调用参数中。
LLM 对象目前不直接支持此功能。
- 蟒
- TypeScript (类型脚本)
# When tracing within LangChain, run names default to the class name of the traced object (e.g., 'ChatOpenAI').
configured_chain = chain.with_config({"run_name": "MyCustomChain"})
configured_chain.invoke({"input": "What is the meaning of life?"})
# You can also configure the run name at invocation time, like below
chain.invoke({"input": "What is the meaning of life?"}, {"run_name": "MyCustomChain"})
// When tracing within LangChain, run names default to the class name of the traced object (e.g., 'ChatOpenAI').
const configuredChain = chain.withConfig({ runName: "MyCustomChain" });
await configuredChain.invoke({ input: "What is the meaning of life?" });
// You can also configure the run name at invocation time, like below
await chain.invoke({ input: "What is the meaning of life?" }, {runName: "MyCustomChain"})
自定义运行 ID
在调用或流式传输 LangChain 代码时,您可以通过在 Config 中提供 ID 来自定义给定运行的 ID。
此 ID 用于唯一标识 LangSmith 中的运行,并可用于查询特定运行。该 ID 可用于链接跨不同系统的运行或实施自定义跟踪逻辑。
这可以通过设置run_id在RunnableConfig对象,或者通过传递run_id在 JS/TS 的调用参数中。
LLM 对象目前不直接支持此功能。
- 蟒
- TypeScript (类型脚本)
import uuid
my_uuid = uuid.uuid4()
# You can configure the run ID at invocation time:
chain.invoke({"input": "What is the meaning of life?"}, {"run_id": my_uuid})
import { v4 as uuidv4 } from 'uuid';
const myUuid = uuidv4();
// You can configure the run ID at invocation time, like below
await chain.invoke({ input: "What is the meaning of life?" }, { runId: myUuid });
请注意,如果您在跟踪的根目录(即顶级运行)执行此作,则该运行 ID 将用作trace_id).
访问 LangChain 调用的运行(跨度)ID
调用 LangChain 对象时,可以访问调用的运行 ID。此运行 ID 可用于查询 LangSmith 中的运行。
在 Python 中,您可以使用collect_runscontext manager 访问运行 ID。
在 JS/TS 中,您可以使用RunCollectorCallbackHandlerinstance 访问运行 ID。
- 蟒
- TypeScript (类型脚本)
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
from langchain_core.tracers.context import collect_runs
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", "You are a helpful assistant. Please respond to the user's request only based on the given context."),
("user", "Question: {question}\n\nContext: {context}")
])
model = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o-mini")
output_parser = StrOutputParser()
chain = prompt | model | output_parser
question = "Can you summarize this morning's meetings?"
context = "During this morning's meeting, we solved all world conflict."
with collect_runs() as cb:
result = chain.invoke({"question": question, "context": context})
# Get the root run id
run_id = cb.traced_runs[0].id
print(run_id)
import { ChatOpenAI } from "@langchain/openai";
import { ChatPromptTemplate } from "@langchain/core/prompts";
import { StringOutputParser } from "@langchain/core/output_parsers";
import { RunCollectorCallbackHandler } from "@langchain/core/tracers/run_collector";
const prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.fromMessages([
["system", "You are a helpful assistant. Please respond to the user's request only based on the given context."],
["user", "Question: {question\n\nContext: {context}"],
]);
const model = new ChatOpenAI({ modelName: "gpt-4o-mini" });
const outputParser = new StringOutputParser();
const chain = prompt.pipe(model).pipe(outputParser);
const runCollector = new RunCollectorCallbackHandler();
const question = "Can you summarize this morning's meetings?"
const context = "During this morning's meeting, we solved all world conflict."
await chain.invoke(
{ question: question, context: context },
{ callbacks: [runCollector] }
);
const runId = runCollector.tracedRuns[0].id;
console.log(runId);
确保在退出之前提交所有跟踪
在 LangChain Python 中,LangSmith 的跟踪是在后台线程中完成的,以避免阻碍您的生产应用程序。这意味着您的进程可能会在所有跟踪成功发布到 LangSmith 之前结束。这在无服务器环境中尤其普遍,在无服务器环境中,一旦链或代理完成,您的 VM 可能会立即终止。
您可以通过设置LANGCHAIN_CALLBACKS_BACKGROUND环境变量设置为"false".
对于这两种语言,LangChain 都公开了等待跟踪提交后再退出应用程序的方法。 下面是一个示例:
- 蟒
- TypeScript (类型脚本)
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain_core.tracers.langchain import wait_for_all_tracers
llm = ChatOpenAI()
try:
llm.invoke("Hello, World!")
finally:
wait_for_all_tracers()
import { ChatOpenAI } from "@langchain/openai";
import { awaitAllCallbacks } from "@langchain/core/callbacks/promises";
try {
const llm = new ChatOpenAI();
const response = await llm.invoke("Hello, World!");
} catch (e) {
// handle error
} finally {
await awaitAllCallbacks();
}
不设置环境变量的跟踪
如其他指南中所述,以下环境变量允许您配置启用的跟踪、api 端点、api 密钥和跟踪项目:
LANGSMITH_TRACINGLANGSMITH_API_KEYLANGSMITH_ENDPOINTLANGSMITH_PROJECT
但是,在某些环境中,无法设置环境变量。在这些情况下,您可以通过编程方式设置跟踪配置。
这在很大程度上建立在上一节的基础上。
- 蟒
- TypeScript (类型脚本)
from langchain.callbacks.tracers import LangChainTracer
from langsmith import Client
# You can create a client instance with an api key and api url
client = Client(
api_key="YOUR_API_KEY", # This can be retrieved from a secrets manager
api_url="https://api.smith.langchain.com", # Update appropriately for self-hosted installations or the EU region
)
# You can pass the client and project_name to the LangChainTracer instance
tracer = LangChainTracer(client=client, project_name="test-no-env")
chain.invoke({"question": "Am I using a callback?", "context": "I'm using a callback"}, config={"callbacks": [tracer]})
# LangChain Python also supports a context manager which allows passing the client and project_name
from langchain_core.tracers.context import tracing_v2_enabled
with tracing_v2_enabled(client=client, project_name="test-no-env"):
chain.invoke({"question": "Am I using a context manager?", "context": "I'm using a context manager"})
import { LangChainTracer } from "@langchain/core/tracers/tracer_langchain";
import { Client } from "langsmith";
// You can create a client instance with an api key and api url
const client = new Client(
{
apiKey: "YOUR_API_KEY",
apiUrl: "https://api.smith.langchain.com", // Update appropriately for self-hosted installations or the EU region
}
);
// You can pass the client and project_name to the LangChainTracer instance
const tracer = new LangChainTracer({client, projectName: "test-no-env"});
await chain.invoke(
{
question: "Am I using a callback?",
context: "I'm using a callback",
},
{ callbacks: [tracer] }
);
使用 LangChain 进行分布式跟踪 (Python)
LangSmith 支持使用 LangChain Python 进行分布式跟踪。这允许您跨不同的服务和应用程序链接运行(跨度)。 其原理类似于 LangSmith SDK 的分布式跟踪指南。
import langsmith
from langchain_core.runnables import chain
from langsmith.run_helpers import get_current_run_tree
# -- This code should be in a separate file or service --
@chain
def child_chain(inputs):
return inputs["test"] + 1
def child_wrapper(x, headers):
with langsmith.tracing_context(parent=headers):
child_chain.invoke({"test": x})
# -- This code should be in a separate file or service --
@chain
def parent_chain(inputs):
rt = get_current_run_tree()
headers = rt.to_headers()
# ... make a request to another service with the headers
# The headers should be passed to the other service, eventually to the child_wrapper function
parent_chain.invoke({"test": 1})
LangChain (Python) 和 LangSmith SDK 之间的互作性
如果您将 LangChain 用于应用程序的一部分,将 LangSmith SDK(请参阅本指南)用于其他部分,您仍然可以无缝地跟踪整个应用程序。
LangChain 对象在traceable函数绑定为traceable功能。
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
from langsmith import traceable
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", "You are a helpful assistant. Please respond to the user's request only based on the given context."),
("user", "Question: {question}\nContext: {context}")
])
model = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o-mini")
output_parser = StrOutputParser()
chain = prompt | model | output_parser
# The above chain will be traced as a child run of the traceable function
@traceable(
tags=["openai", "chat"],
metadata={"foo": "bar"}
)
def invoke_runnnable(question, context):
result = chain.invoke({"question": question, "context": context})
return "The response is: " + result
invoke_runnnable("Can you summarize this morning's meetings?", "During this morning's meeting, we solved all world conflict.")
这将生成以下跟踪树: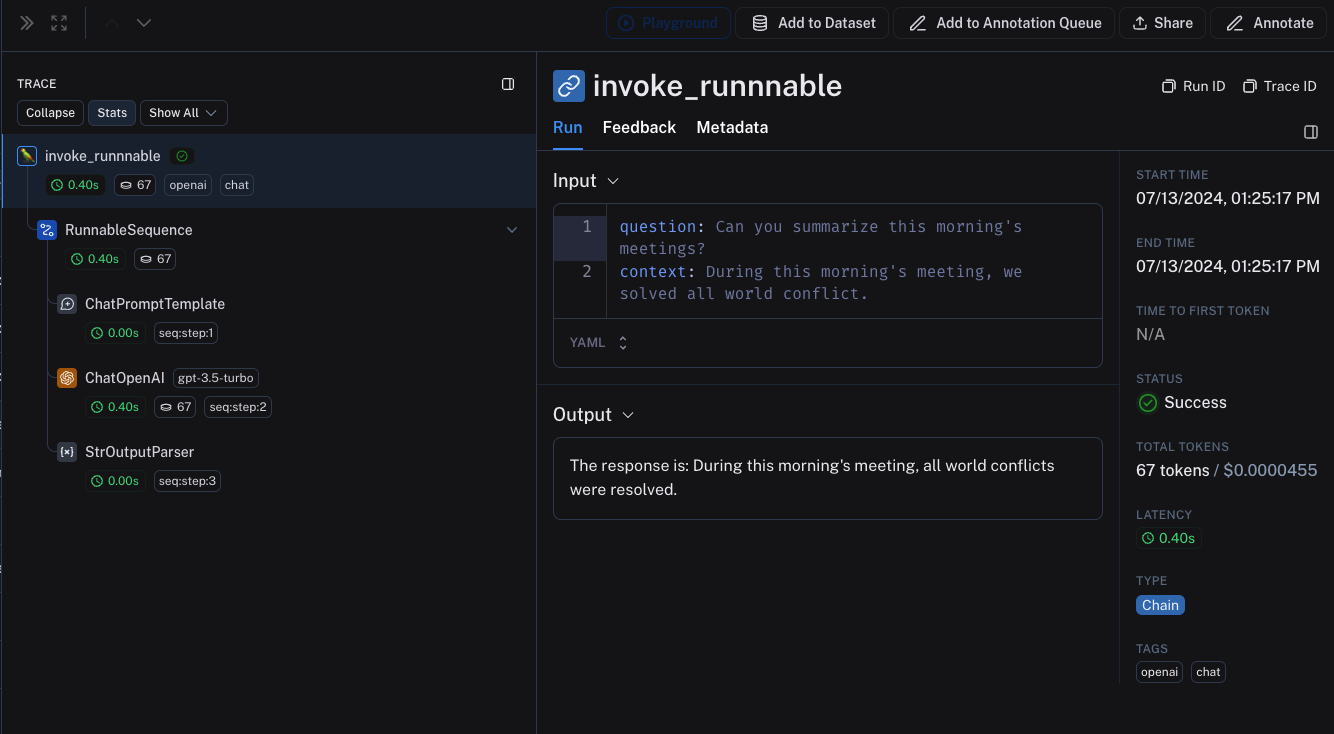
LangChain.JS 和 LangSmith SDK 之间的互作性
跟踪内部的 LangChain 对象traceable(仅限 JS)
起始langchain@0.2.x,则 LangChain 对象在内部使用@traceable函数,继承可追溯函数的客户端、标签、元数据和项目名称。
对于下面的旧版本的 LangChain0.2.x中,您需要手动传递一个实例LangChainTracer根据 中找到的跟踪上下文创建@traceable.
import { ChatOpenAI } from "@langchain/openai";
import { ChatPromptTemplate } from "@langchain/core/prompts";
import { StringOutputParser } from "@langchain/core/output_parsers";
import { getLangchainCallbacks } from "langsmith/langchain";
const prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.fromMessages([
[
"system",
"You are a helpful assistant. Please respond to the user's request only based on the given context.",
],
["user", "Question: {question}\nContext: {context}"],
]);
const model = new ChatOpenAI({ modelName: "gpt-4o-mini" });
const outputParser = new StringOutputParser();
const chain = prompt.pipe(model).pipe(outputParser);
const main = traceable(
async (input: { question: string; context: string }) => {
const callbacks = await getLangchainCallbacks();
const response = await chain.invoke(input, { callbacks });
return response;
},
{ name: "main" }
);
跟踪 LangChain 子级运行traceable/ RunTree API(仅限 JS)
我们正在努力提高traceable和 LangChain 的 LangChain 中。将 LangChain 与 结合使用时,存在以下限制traceable:
- 修改 RunTree 从
getCurrentRunTree()的 RunnableLambda 上下文将导致无作。 - 不建议遍历从 RunnableLambda 获取的 RunTree
getCurrentRunTree(),因为它可能不包含所有 RunTree 节点。 - 不同的子运行可能具有相同的
execution_order和child_execution_order价值。因此,在极端情况下,某些运行可能会以不同的顺序结束,具体取决于start_time.
在某些使用案例中,您可能希望运行traceable函数作为 RunnableSequence 的一部分运行,或者跟踪 LangChain 的子运行通过RunTree应用程序接口。从 LangSmith 0.1.39 和 @langchain/core 0.2.18 开始,您可以直接调用traceable-wrapped 函数。
import { traceable } from "langsmith/traceable";
import { RunnableLambda } from "@langchain/core/runnables";
import { RunnableConfig } from "@langchain/core/runnables";
const tracedChild = traceable((input: string) => `Child Run: ${input}`, {
name: "Child Run",
});
const parrot = new RunnableLambda({
func: async (input: { text: string }, config?: RunnableConfig) => {
return await tracedChild(input.text);
},
});
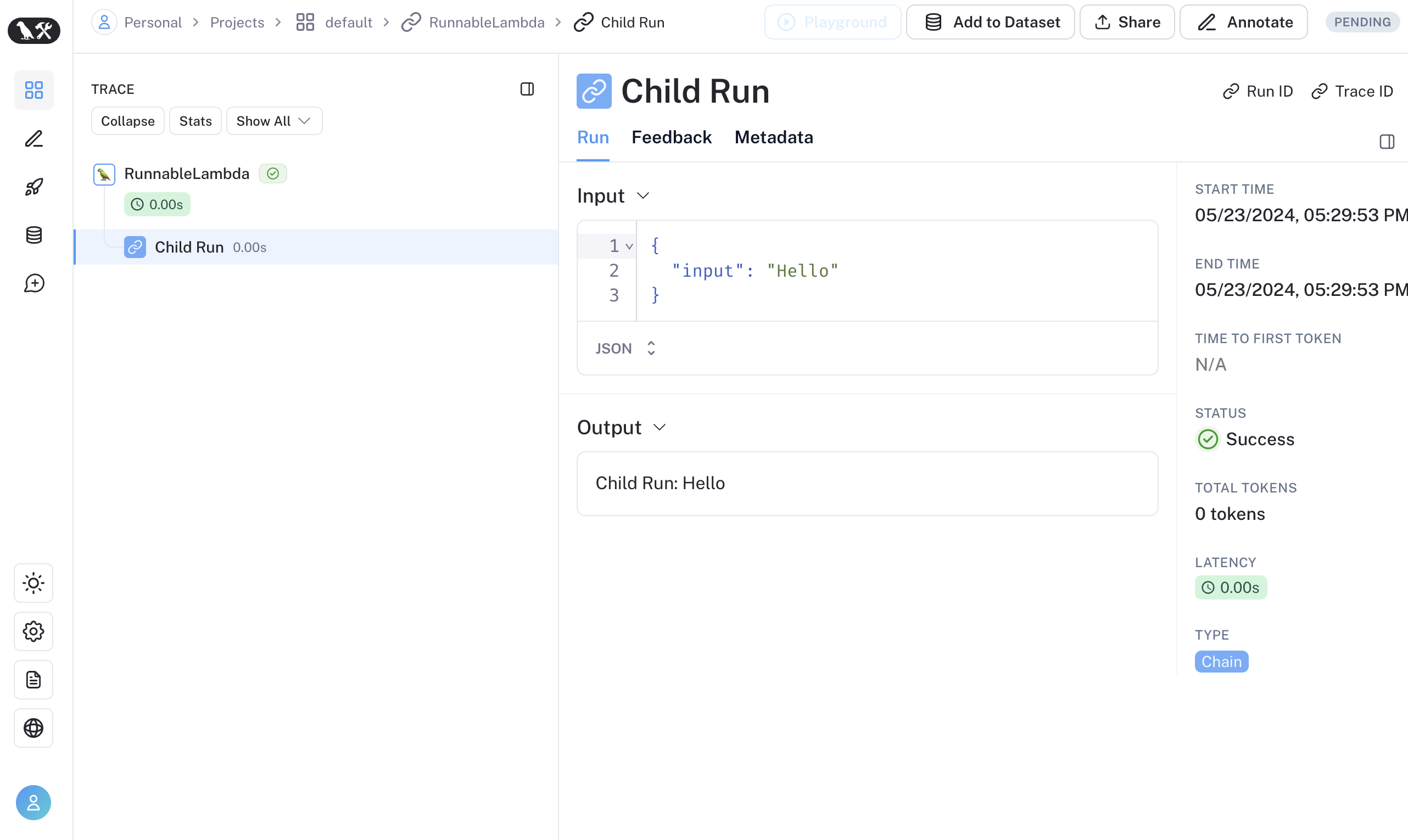
或者,你可以将 LangChain 的RunnableConfig使用等效的 RunTree 对象RunTree.fromRunnableConfig或将RunnableConfig作为traceable-wrapped 函数。
- 溯源
- Run Tree
import { traceable } from "langsmith/traceable";
import { RunnableLambda } from "@langchain/core/runnables";
import { RunnableConfig } from "@langchain/core/runnables";
const tracedChild = traceable((input: string) => `Child Run: ${input}`, {
name: "Child Run",
});
const parrot = new RunnableLambda({
func: async (input: { text: string }, config?: RunnableConfig) => {
// Pass the config to existing traceable function
await tracedChild(config, input.text);
return input.text;
},
});
import { RunTree } from "langsmith/run_trees";
import { RunnableLambda } from "@langchain/core/runnables";
import { RunnableConfig } from "@langchain/core/runnables";
const parrot = new RunnableLambda({
func: async (input: { text: string }, config?: RunnableConfig) => {
// create the RunTree from the RunnableConfig of the RunnableLambda
const childRunTree = RunTree.fromRunnableConfig(config, {
name: "Child Run",
});
childRunTree.inputs = { input: input.text };
await childRunTree.postRun();
childRunTree.outputs = { output: `Child Run: ${input.text}` };
await childRunTree.patchRun();
return input.text;
},
});
如果您更喜欢视频教程,请观看 LangSmith 课程简介中的跟踪替代方法视频。