优化分类器
本教程介绍如何根据用户反馈优化分类器。 分类器非常适合优化,因为收集所需的输出通常非常简单,这使得根据用户反馈创建少量镜头示例变得容易。 这正是我们在此示例中将要执行的作。
目标
在此示例中,我们将构建一个机器人,根据 GitHub 问题的标题对 GitHub 问题进行分类。 它将接收一个标题并将其分类为许多不同的类别之一。 然后,我们将开始收集用户反馈,并使用它来塑造这个分类器的执行方式。
开始
首先,我们首先对其进行设置,以便将所有跟踪发送到特定项目。 我们可以通过设置一个环境变量来实现这一点:
import os
os.environ["LANGSMITH_PROJECT"] = "classifier"
然后,我们可以创建初始应用程序。这将是一个非常简单的函数,它只接收 GitHub 问题标题并尝试标记它。
import openai
from langsmith import traceable, Client
import uuid
client = openai.Client()
available_topics = [
"bug",
"improvement",
"new_feature",
"documentation",
"integration",
]
prompt_template = """Classify the type of the issue as one of {topics}.
Issue: {text}"""
@traceable(
run_type="chain",
name="Classifier",
)
def topic_classifier(
topic: str
):
return client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o-mini",
temperature=0,
messages=[
{
"role": "user",
"content": prompt_template.format(
topics=','.join(available_topics),
text=topic,
)
}
],
).choices[0].message.content
然后我们可以开始与它交互。 与它交互时,我们将提前生成 LangSmith 运行 ID 并将其传递给此函数。 我们这样做是为了以后可以附加反馈。
以下是调用应用程序的方法:
run_id = uuid.uuid4()
topic_classifier(
"fix bug in LCEL",
langsmith_extra={"run_id": run_id}
)
以下是我们之后如何附加反馈。 我们可以通过两种形式收集反馈。
首先,我们可以收集 “积极” 反馈 - 这是模型正确的例子。
ls_client = Client()
run_id = uuid.uuid4()
topic_classifier(
"fix bug in LCEL",
langsmith_extra={"run_id": run_id}
)
ls_client.create_feedback(
run_id,
key="user-score",
score=1.0,
)
接下来,我们可以专注于收集与对这一代的 “更正” 相对应的反馈。 在这个例子中,模型会将其归类为 bug,而我真的希望将其归类为 documentation。
ls_client = Client()
run_id = uuid.uuid4()
topic_classifier(
"fix bug in documentation",
langsmith_extra={"run_id": run_id}
)
ls_client.create_feedback(
run_id,
key="correction",
correction="documentation"
)
设置自动化
我们现在可以设置自动化,将带有某种形式反馈的示例移动到数据集中。 我们将设置两个自动化,一个用于正面反馈,另一个用于负面反馈。
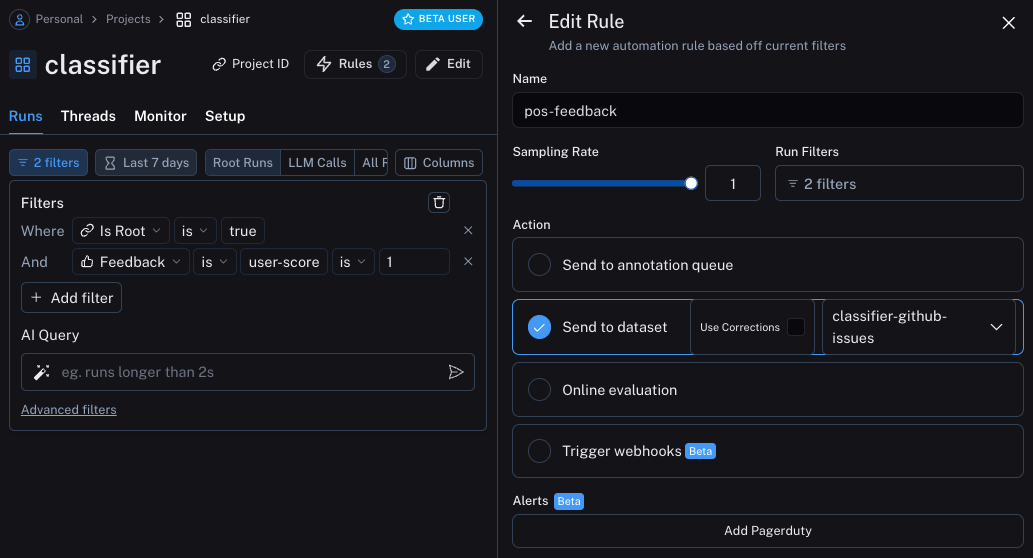
第一个选项将获取所有具有积极反馈的运行,并自动将它们添加到数据集中。
这背后的逻辑是,任何具有积极反馈的运行都可以在未来的迭代中用作一个很好的示例。
让我们创建一个名为classifier-github-issues将此数据添加到。
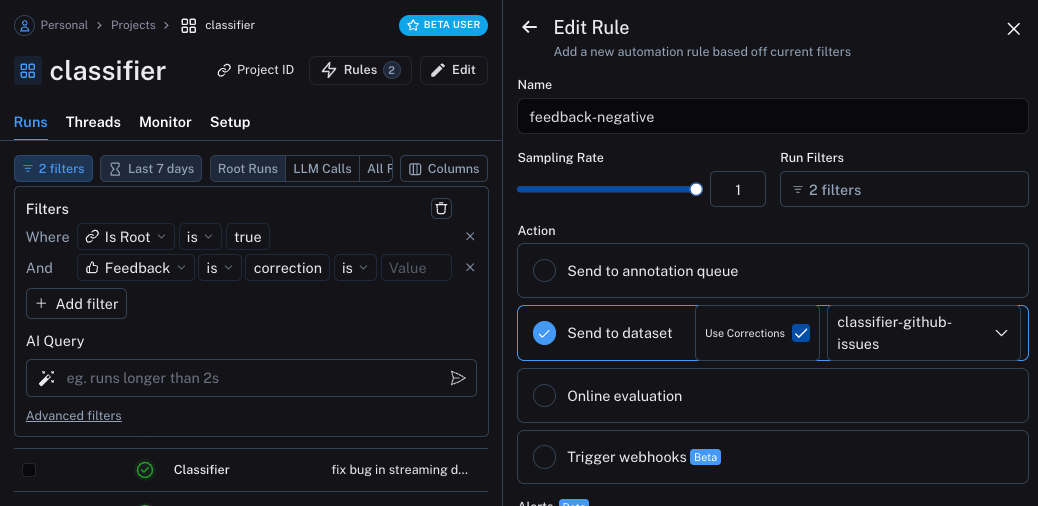
第二个选项将获取所有带有校正的运行,并使用 webhook 将其添加到数据集中。 创建此 webhook 时,我们将选择“使用更正”选项。 此选项将使从运行创建数据集时,而不是使用运行的输出 作为数据点的 gold-truth 输出,它将使用 correction。
更新应用程序
现在,我们可以更新代码以拉取要将运行发送到的数据集。 一旦我们拉取它,我们就可以创建一个包含示例的字符串。 然后,我们可以将此字符串作为 Prompt!
### NEW CODE ###
# Initialize the LangSmith Client so we can use to get the dataset
ls_client = Client()
# Create a function that will take in a list of examples and format them into a string
def create_example_string(examples):
final_strings = []
for e in examples:
final_strings.append(f"Input: {e.inputs['topic']}\n> {e.outputs['output']}")
return "\n\n".join(final_strings)
### NEW CODE ###
client = openai.Client()
available_topics = [
"bug",
"improvement",
"new_feature",
"documentation",
"integration",
]
prompt_template = """Classify the type of the issue as one of {topics}.
Here are some examples:
{examples}
Begin!
Issue: {text}
>"""
@traceable(
run_type="chain",
name="Classifier",
)
def topic_classifier(
topic: str
):
# We can now pull down the examples from the dataset
# We do this inside the function so it always get the most up-to-date examples,
# But this can be done outside and cached for speed if desired
examples = list(ls_client.list_examples(dataset_name="classifier-github-issues")) # <- New Code
example_string = create_example_string(examples)
return client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o-mini",
temperature=0,
messages=[
{
"role": "user",
"content": prompt_template.format(
topics=','.join(available_topics),
text=topic,
examples=example_string,
)
}
],
).choices[0].message.content
如果现在使用与以前类似的输入运行应用程序,我们可以看到它正确地学习了与 docs 相关的任何内容(即使是 bug)都应该被归类为documentation
ls_client = Client()
run_id = uuid.uuid4()
topic_classifier(
"address bug in documentation",
langsmith_extra={"run_id": run_id}
)
对示例进行语义搜索
我们可以做的另一件事是只使用语义上最相似的示例。 当您开始构建大量示例时,这非常有用。
为此,我们首先可以定义一个示例来查找k最相似的例子:
import numpy as np
def find_similar(examples, topic, k=5):
inputs = [e.inputs['topic'] for e in examples] + [topic]
vectors = client.embeddings.create(input=inputs, model="text-embedding-3-small")
vectors = [e.embedding for e in vectors.data]
vectors = np.array(vectors)
args = np.argsort(-vectors.dot(vectors[-1])[:-1])[:5]
examples = [examples[i] for i in args]
return examples
然后,我们可以在应用程序中使用它
ls_client = Client()
def create_example_string(examples):
final_strings = []
for e in examples:
final_strings.append(f"Input: {e.inputs['topic']}\n> {e.outputs['output']}")
return "\n\n".join(final_strings)
client = openai.Client()
available_topics = [
"bug",
"improvement",
"new_feature",
"documentation",
"integration",
]
prompt_template = """Classify the type of the issue as one of {topics}.
Here are some examples:
{examples}
Begin!
Issue: {text}
>"""
@traceable(
run_type="chain",
name="Classifier",
)
def topic_classifier(
topic: str
):
examples = list(ls_client.list_examples(dataset_name="classifier-github-issues"))
examples = find_similar(examples, topic)
example_string = create_example_string(examples)
return client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o-mini",
temperature=0,
messages=[
{
"role": "user",
"content": prompt_template.format(
topics=','.join(available_topics),
text=topic,
examples=example_string,
)
}
],
).choices[0].message.content